Whether upgrading your CPU Cooler or buying it for the first time for your new PC, you need to ensure that the CPU Cooler you are getting is fully compatible with your PC to avoid hassles and performance issues. Choosing the right CPU Cooler (Air Cooler or AIO Liquid Cooler) is very important if you don’t want to lose your hard-earned money, effort, and precious time. CPU Cooler is one of the most important components of a PC because it can directly impact the performance of your CPU and the entire PC. Many factors and parameters come into play when selecting the CPU Cooler; if one is neglected, you can be in a great deal of trouble. So, to help you with this issue, I am listing the critical factors and parameters you must keep in mind to ensure that your CPU cooler has no compatibility issues with your CPU and PC.
Socket Support [For Air and AIO Cooler]
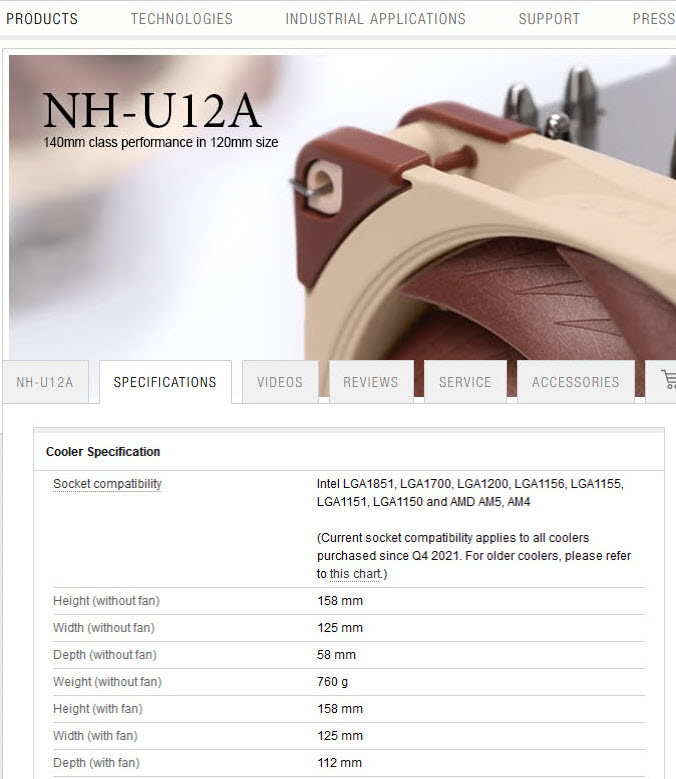
The first thing to check for CPU Cooler compatibility with your CPU is the socket support. If the CPU Cooler you are getting does not support or is compatible with the socket of your CPU, then it is a complete waste of time and money because you won’t be able to mount that CPU Cooler on your CPU and motherboard. For example, if you have AMD Ryzen 7 7800X CPU having AM5 Socket but the CPU Cooler that you have selected supports only up to AM4 Socket, then you can’t use that CPU Cooler with your CPU unless the CPU Cooler manufacturer releases an AM5 bracket. You can check the sockets supported by the CPU Cooler on its product specifications page by visiting the Cooler’s manufacturer’s website. For example, if you select Noctua NH-U12A CPU Air Cooler, you can check the supported CPU Sockets on the product specifications page below. The image shows that the Noctua NH-U12A CPU Air Cooler supports all the latest Intel and AMD CPU Sockets, including the AMD AM5 Socket.
PC Case Support and Clearance
For CPU Air Cooler
Height of the CPU Cooler – When selecting a CPU Air Cooler for your CPU, the second most important thing to look for after socket compatibility is the height of the CPU Cooler (with Fan). Each PC Case has a different level of CPU Cooler Height clearance, and if your Cooler Height is more than what the PC Case supports, then the CPU Cooler won’t fit in the PC Case. For example, if your PC Case supports a CPU Air Cooler with up to 155mm in height and the CPU Cooler you have selected is 162mm tall, then you can have issues fitting that CPU Cooler in your Case.
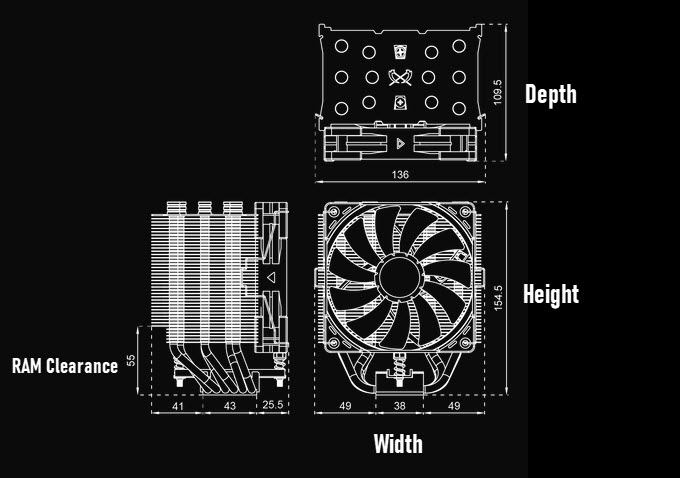
Width of the CPU Cooler – Regarding dimensions, the width of the CPU Air Cooler should also be considered for its compatibility with the PC Case. Some motherboards can have big heatsinks or components near the CPU Socket and can interfere with the CPU Cooler if the width of the CPU Cooler is greater. So, if you have this kind of issue, you should also consider the width of the CPU Cooler to avoid any kind of clearance issue related to dimensions in the PC Case.
For AIO Liquid Cooler
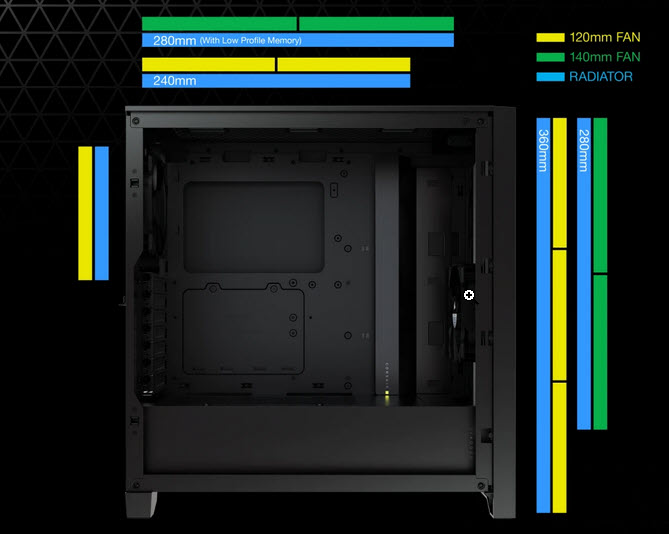
Radiator Size Support – If you are getting an AIO Cooler, your PC Case should support the radiator size of your AIO CPU Cooler. For example, if your PC Case supports Radiators up to only 280mm in length and you are considering a 360mm AIO, then this AIO will not fit in your PC Case. The image below is for the Corsair 4000D AIRFLOW Tempered Glass Mid-Tower ATX Case Radiator Support for AIO CPU Cooler.

RAM Clearance [For CPU Air Cooler]
Big or Dual-Tower CPU Air Coolers may interfere with the RAM with taller heatsinks. If you have low-profile RAM with slim heatsinks or RAM with no heatsinks, then you don’t have to worry about Big CPU Air Coolers interfering with your RAM. So, if you have RAM with heatsinks, you must check the CPU RAM Clearance on its product specifications page to avoid compatibility issues when installing the CPU Cooler.

Graphics Card Clearance [For CPU Air Cooler]
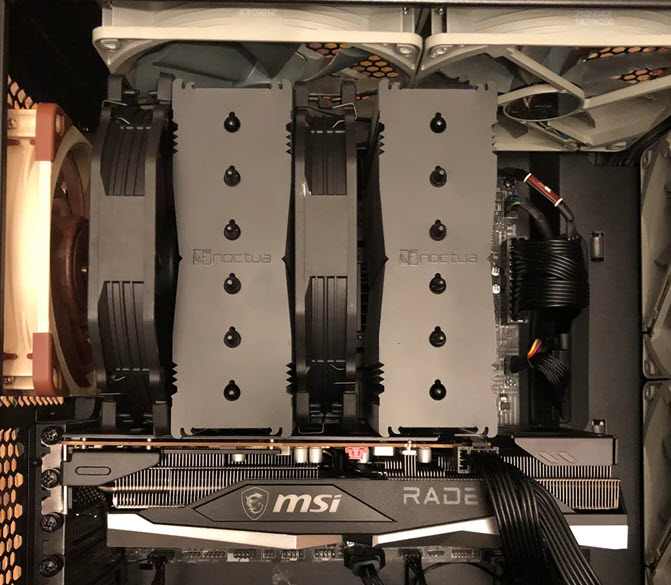
Some high-end graphics cards may have a fancy or thicker backplate that may interfere with a CPU Cooler with a bigger heatsink or greater depth. If the CPU Cooler barely touches the graphics card backplate, then this is not a sign of worry. However, if the contact is more significant and the CPU cooler heatsink pushes the graphics card downwards, then it can cause damage to your graphics card’s PCB/PCIe x16 connector or motherboard PCIe x16 slot. In such a scenario, the bending of the graphics card can cause its PCB to crack, and if the crack goes deep into the layers, then in most cases, the card cannot be repaired. Moreover, the vibrations from the CPU Cooler heatsink can cause damage to the graphics card backplate, especially if it is a plastic backplate. Below, you can see a dual-tower CPU Cooler making contact with the graphics card.
Motherboard Fan Headers [For AIO]
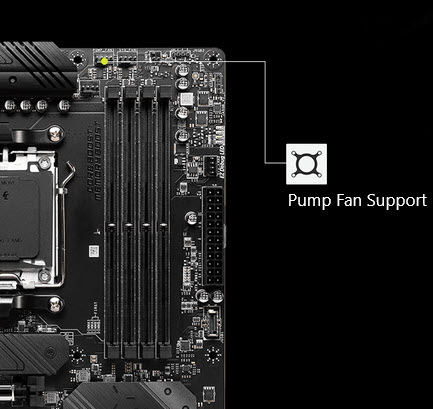
If your motherboard does not have enough 4-pin headers required for the AIO you are getting, you may have issues. Generally, modern motherboards come with enough 4-pin headers, including a pump header. However, if your motherboard does not have enough 4-pin headers for AIO and Case Fans, you have to select another CPU cooler or use a compatible fan hub.

Cooling Capacity of CPU Cooler
If you have done everything right to ensure that your computer case supports your CPU cooler but ignored the CPU Cooler cooling capacity, then you may run into problems regarding CPU performance or overheating. The Cooling Capacity of a CPU Cooler is the maximum amount of heat that the CPU Cooler can dissipate without causing CPU overheating. It is measured in Watts. For example, if the cooling capacity of the CPU Cooler is 65W but your CPU TDP (Thermal Design Power) is 95W, then installing this CPU Cooler can cause overheating and thermal throttling of your CPU, and this will result in reduced performance and shorting of the lifespan of your CPU. Generally, the cooling capacity of the CPU cooler is not mentioned by the manufacturer, but you can get a rough estimate of this figure by checking the CPU cooler reviews on reputed hardware websites.
Note: TDP of the CPU is the maximum amount of heat generated by the CPU or power consumption of the CPU under heavy or maximum load. The TDP is measured in Watts (W).
See also:
Need Help?
If you need help regarding CPU Cooler compatibility or suggestions for the best CPU Cooler for your CPU and PC, then you can ask me your queries in the comment section below.
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through the links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)
![Best H470 Motherboard for Intel 10th Gen Processors [LGA 1200 Socket] Best H470 Motherboard for Intel 10th Gen Processors [LGA 1200 Socket]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/GIGABYTE-H470-AORUS-PRO-AX-211x150.jpg)
![Best Gaming Hard Drive for Gaming PC [3.5 inch Internal HDD] Best Gaming Hard Drive for Gaming PC [3.5 inch Internal HDD]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/gaming-hard-drive-211x150.jpg)
![Best X299 Motherboard for Intel Core-X Processors [LGA 2066 Socket] Best X299 Motherboard for Intel Core-X Processors [LGA 2066 Socket]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/best-x299-motherboard-lga-2066-socket-211x150.jpg)