Thermal Interface Material (TIM) is a substance that is used to fill the gaps between the heatsink and the chip for better and more efficient heat transfer. The performance of a Thermal Interface Material (TIM) depends on its ability to fill the gaps between the heatsink and chip, the thermal conductivity of the thermal interface material, and its lifespan or rate of degradation over time. The two most commonly used thermal interface materials are Thermal Paste and Thermal Pads for use with CPU, GPU, VRAM, VRM, IC, etc., but now a new thermal interface material called Phase Change Material (PCM) is becoming gaining popularity because of its superior properties over traditional thermal paste and thermal pads.
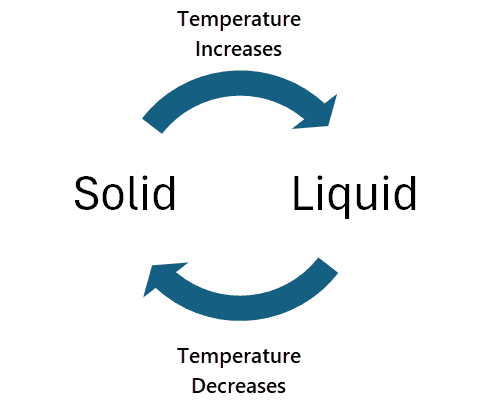
Phase Change Thermal Interface Material (TIM) or Phase Change Material (PCM) is a game-changing product in PC Cooling solutions. Phase Change Material (PCM) is a special type of thermal interface material that changes its physical state from one to another with a change in temperature. Phase Change Material is solid at room temperature and begins to change its state to liquid and flow at higher temperatures. When the temperature decreases, it changes from liquid to solid. The temperature at which the transition of states occurs from solid to liquid and then again to solid may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. Phase Change material is available in Pad/Sheet and Paste form, but the Pad version is the most popular and widely used, mainly in PC Cooling applications, the automotive industry, and enterprise solutions.
How Phase Change Material (PCM) Works
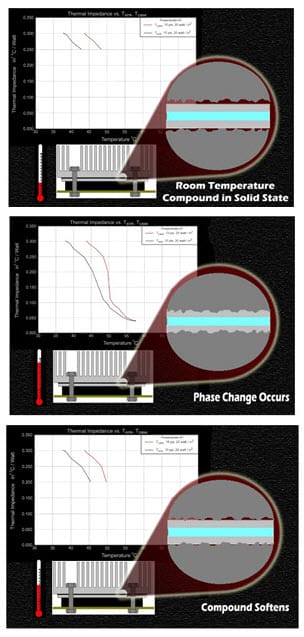
At room temperature, the phase change material (PCM) is in the solid state. When the CPU/GPU temperature increases, the PCM begins to melt at 45°C and convert into a liquid state with low viscosity. In the liquid state, the material fills all the micro gaps and pores between the heatsink and the chip (CPU/GPU). When the temperature decreases, the phase change material begins to solidify, leading to a uniform layer of material, leaving no gaps behind.
It should be noted that the maximum performance of phase change material can be seen after a few thermal cycles with a temperature above 60°C. You also need to apply an extra amount of mounting force or pressure when installing phase change material between the heatsink and the source chip (CPU/GPU) so that when the phase change material melts, the gap between the heatsink and the chip should be as minimal as possible.
Phase Change Thermal Interface Material Applications
The phase change material (PCM) in PCs is most commonly used for high-end CPUs and GPUs. It is also used for CPUs and GPUs in laptops, gaming consoles (PS4/PS5/PlayStation, etc.), and automotive and enterprise solutions. Below, you can see the PTM7950 Phase Change Pad being applied to a laptop.

Phase Change Material Advantages and Disadvantages
Below are the advantages and disadvantages of using a phase change thermal interface material.
Advantages of Phase Change Material
Longer Lifespan and No Dry-Out Issue – Phase Change Material (PCM) has a much longer lifespan than traditional thermal pastes. Even a good thermal paste can dry out after a few years, especially under continuous heavy workloads or temperatures. However, phase change thermal material retains its phase change properties for the entire lifespan of your device or component.
No Pump-out Issue – One of the main benefits of using a phase change thermal pad is that it does not suffer from the pump-out effect. Traditional thermal pastes suffer from a very serious issue known as the pump-out effect. With the pump-out effect, the thermal paste is slowly pressed out between the heatspreader and the base plate of the CPU cooler. The temperatures under load cause the heatspreader and the base plate (mainly the copper baseplate) to deform (concave or convex) and return to their original shape (straight) when they cool down, causing the thermal paste to squeeze out from the side slowly. This can result in higher CPU/GPU temperatures, overheating, and a significant drop in performance, as thermal throttling can occur, reducing the frequency/clock of the chip (CPU/GPU). The Pump-out effect is minimal or does not occur with phase change material as it contracts, regains its shape, and converts into solid form when the temperature decreases.
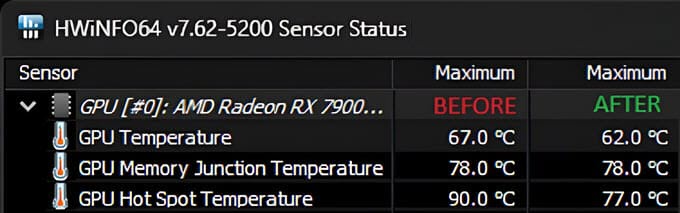
Excellent Performance – The performance of phase change material is outstanding and may outperform some of the best thermal pastes in the market, including Arctic MX-4, Noctua NT-H1, Thermal Grizzly Kryonaut, etc. The performance of phase change material gets better with time as it goes through more and more thermal cycles. You can expect a further 2 to 3 degrees Celsius drop in temperature as the PCM gets fully cooked and fills all gaps permanently. Moreover, on a GPU, you can expect a significant reduction in GPU hotspot temperatures compared to thermal pastes.
Electrically Non-conductive – Phase Change Thermal is electrically non-conductive, so you don’t have to worry about short-circuiting if it comes in contact with SMD components on the motherboard or PCB.
Disadvantages of Phase Change Material
Difficult to Apply – Even though it seems easy to apply, the reality is totally opposite. Phase Change Thermal Material is quite challenging to apply compared to traditional thermal paste and thermal pads. The phase change material is relatively thin (0.20 to 0.25mm) and flexible, and laying it uniformly on a chip and processor (CPU/GPU) is quite challenging. However, once you have done it correctly, there is no going back, as you don’t have to replace it again because it lasts very long.
Note: Some users suggest keeping the phase change material in a fridge for a few minutes so that it becomes a bit hard and can be easily applied to a chip or processor becomes easy.
Expensive – Phase Change Thermal Interface Material costs way more than a high-end thermal paste (non-conductive).
Hard to Get – Some Phase Change Thermal Materials are very hard to get, and many fakes are available online. Getting a genuine product at a reasonable cost is a bit of a challenge.
Better Performers Available – Although the performance of phase change material is outstanding, it is not as good as liquid metal thermal paste or graphene thermal pads (e.g., Thermal Grizzly KryoSheet).
Best Phase Change Thermal Pads
Here are the top Phase Change Thermal Pads for processors, including CPUs and GPUs.
Honeywell PTM7950 Phase Change Pad
Honeywell PTM7950 Phase Change Pad is the most popular phase change pad OEMs use in their electronic components, devices, or computing solutions. Honeywell PTM7950 is available in 0.25mm and 0.20mm thicknesses, where the 0.25mm thick one is more common. The pad is grey in color and is available in various sizes depending on your requirements or needs. The material’s thermal conductivity is 8.5 W/mk, and it is electrically non-conductive and has very low thermal impedance.

Honeywell PTM7950 is based on a novel polymer PCM system; PTM7950 exhibits excellent interface wettability during typical operating temperature ranges, resulting in extremely low surface contact resistance. It is Silicone-free, has no pump-out, bleed-out, or dry-out issues, and lasts very long. Nowadays, the PTM7950 Phase Change Pad is being used in most high-end Nvidia and AMD graphics cards (RTX 50 series and RX 9000 series) by some AIB partners like Asus.
| Honeywell PTM7950 Phase Change Pad Specifications | |
| Size | 31×50, 40×80, 80×80 (mm) and more custom sizes available |
| Thickness | 0.25mm / 0.20mm |
| Color | Grey |
| Thermal Conductivity | 8.5 W/mk |
| Electrically Conductive | No |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C to +125°C |
Buy Honeywell PTM7950 Phase Change Pad
Thermalright Heilos Solid Thermal Interface Sheet V2
Thermalright Heilos Solid Thermal Interface Sheet V2 is an excellent alternative to the Honeywell PTM7950 thermal pad. It is 0.25mm thick and is available in 40x50mm and 40x60mm sizes. The pad has a thermal conductivity of 8.5 W/mk and is gray in color. It is electrically non-conductive and almost identical to the Honeywell PTM7950 pad in terms of properties and performance.

| Thermalright Heilos Solid Thermal Interface Sheet V2 Specifications | |
| Size | 40x50mm, 40x60mm |
| Thickness | 0.25mm |
| Color | Gray |
| Thermal Conductivity | 8.5 W/mk |
| Electrically Conductive | No |
| Operating Temperature | No Specified |
Buy Thermalright Heilos Solid Thermal Interface Sheet V2
Thermal Grizzly PhaseSheet PTM
A very good Phase Change Material (PCM) from a highly reputed brand, Thermal Grizzly. Thermal Grizzly PhaseSheet PTM Thermal Pad is only 0.20mm thick and is available in 50 x 40mm size. It is not electrically conductive and is used for processors and graphics chips.

| Thermal Grizzly PhaseSheet PTM Specifications | |
| Size | 50 x 40mm |
| Thickness | 0.20 mm |
| Color | Grey |
| Thermal Conductivity | 8.5 W/mk (expected) |
| Electrically Conductive | No |
| Operating Temperature | -75°C to +150°C |
Buy Thermal Grizzly PhaseSheet PTM
Final Words
Well, there is no doubt that Phase Change Material (PCM) is better than traditional thermal pastes in terms of longevity and pump-out effect, which is almost non-existent in phase change material. The thermal performance of phase change thermal interface material is also slightly better than that of thermal pastes. Phase Change Material (PCM) can be used for both CPU/Processors and GPU, and they do not need regular replacement because of their much longer lifespan. So, if you do not want to change your thermal interface material often, then Phase Change Material (PCM) is the right choice for you, as you do not have to worry about it getting degraded over time, and you will also get excellent thermal performance, which even gets better with time.
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through the links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)

![Best Mechanical Keyboard Keycaps [PBT, ABS, Translucent, Custom] Best Mechanical Keyboard Keycaps [PBT, ABS, Translucent, Custom]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/mechanical-keyboard-keycaps-211x150.jpg)
