Vega and Pascal are the two latest GPU architectures from AMD and Nvidia respectively. These two GPU architectures are used in some of the most advanced and fastest graphics cards available today. Vega is a relatively newer GPU architecture compared to Pascal from Nvidia. Both these GPU architectures come with their own sets of features and specifications, and here I am going to compare both these GPU architectures and will tell you almost everything about them. You may also check out the comparison of Pascal and Polaris GPU architectures by going to the link given below.
Must Read:
AMD Vega GPU Architecture
Vega is the latest GPU architecture from AMD that is used for both gaming and workstation graphics cards. The gaming graphics cards series built on Vega architecture is the Radeon RX Vega series which has Radeon RX Vega 56 and Radeon RX Vega 64 graphics cards in it. The first graphics card using Vega architecture is the Radeon Vega Frontier Edition which is a powerful workstation graphics card.

Vega is the successor of the Polaris GPU architecture from AMD. The pixel processors used in the latest AMD GPU architectures are known as Stream Processors whether it is Vega or Polaris GPU architecture. These Stream Processors or pixel processing units do all the main work in GPU and the power of graphics cards depends on them. A graphics card with a higher number of Stream Processors is more powerful than a graphics card with a lesser number of Stream Processors, given that both graphics cards are in the same series. Vega is built using the 14nm FinFET manufacturing process and is also known as GCN 5th generation architecture from AMD. GCN stands for Graphics Core Next.
Vega uses HBM2 memory which is one of the fastest memories available today and is used for VR and high bandwidth operations. HBM2 is a stacked memory that uses less space, has lower power consumption, and is even faster than the GDDR5X memory which is used in the high-end Pascal-based gaming graphics cards from Nvidia.
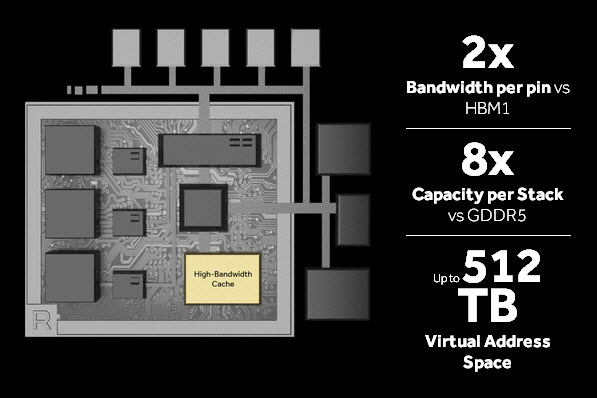
The successor of the Vega Architecture will be Navi Architecture or GCN 6th generation architecture and is expected to be launched in 2018.
Vega Graphics Cards: Radeon Vega RX 64, Radeon Vega RX 56, Radeon Frontier Edition
Major Features of Vega GPU Architecture
- HBM2 Memory
- More Pixel Processors
- Next-Gen Compute Units (NCM)
- FreeSync 2
- Higher Clock Speeds
- VR Ready
- CrossFire support
- Higher Compute Performance
- DirectX 12 / OpenGL 4.5 / Vulkan support
Nvidia Pascal GPU Architecture
Pascal is an advanced GPU architecture from Nvidia that is used in the GeForce 10 series gaming graphics cards and P series Quadro workstation graphics cards. Pascal is the successor to the Maxwell GPU architecture. The pixel processors here are known as CUDA Cores and their number depicts the power of the GPU. A graphics card with a higher number of CUDA Cores in the same series is more powerful than the one with a lesser number of CUDA Cores.
Must Read: CUDA Cores vs Stream Processors Explained
Pascal GPU Architecture uses the 16nm and 14nm FinFET manufacturing process. High-end and mid-range Pascal graphics cards are built on the 16nm manufacturing processor while less powerful and budget Pascal graphics cards are built on the 14nm process. Memory supported by Pascal GPU architecture includes GDDR5, GDDR5X, and HBM2. Only the high-end workstation graphics cards use HBM2 memory while gaming graphics cards in GeForce 10 series use GDDR5 and GDDR5X memory. GDDR5X memory is faster than the normal GDDR5 memory and is used in high-end graphics cards like Nvidia Titan Xp, GeForce GTX 1080 Ti, and GeForce GTX 1080.

Pascal-based graphics cards use less power compared to the Vega graphics cards in the same price and performance segment. For example, GeForce GTX 1080 and Radeon RX Vega 64 are in the same league but the maximum power consumption of Geforce GTX 1080 is 150W (TDP) which is much lower than of Radeon RX Vega which has a TDP of 295W. Similarly is the case with the GeForce GTX 1070 and Radeon RX Vega 56, where Geforce GTX 1070 has a power consumption of 150W max and Radeon RX Vega 56 consumes 210W of power. The successor of Pascal GPU architecture is Volta GPU architecture.
Popular Pascal Graphics Cards: GeForce GTX 1080 Ti, GeForce GTX 1080, GeForce GTX 1070, GeForce GTX 1060, GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, GeForce GTX 1030.
Major Features of Pascal GPU Architecture
- Lower Power Consumption
- VR Ready
- GDDR5X & HBM2 support
- G-Sync
- SLI support (on high-end cards only)
- NVLink
- DirectX 12 / OpenGL 4.5 / Vulkan support
Vega vs Pascal Architecture Comparison
Here in the table, you can see the comparison of Vega and Pascal GPU architectures based on their features and specifications.
| Architecture / Specs | AMD Vega | Nvidia Pascal |
| GPU Manufacturer | AMD | Nvidia |
| Graphics Cards | Radeon RX Vega series | GeForce 10 series |
| Fabrication Process | 14nm | 16nm / 14nm |
| Memory support | HBM2 | GDDR5, GDDR5X, HBM2 |
| VR Support | Yes | Yes |
| Refresh Rate Technology | FreeSync 2 | G-Sync |
| DirectX | 12 | 12 |
| OpenGL | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| Vulkan | Yes | Yes |
| Multi-GPU support | Yes, CrossFire | Yes, SLI (on high-end cards only) |
| Power Consumption | Higher than Pascal | Lower |
| Predecessor | Polaris | Maxwell |
| Successor | Navi | Volta |
Final Words
Well both these GPU architectures are designed for churning out maximum performance in the latest games. Pascal GPU architecture is more energy efficient while Vega is a bit of a power hog. Both are powerful and advanced GPU architectures and they work differently behind the scenes. Pascal GPU architecture can be seen in entry-level and mid-range graphics cards too but currently, Vega architecture is only for high-end graphics cards. If you have any queries or want to express your views then please leave a comment below.
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through the links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)

![What PSU do I Need? [Complete Guide for Beginners] What PSU do I Need? [Complete Guide for Beginners]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/what-psu-do-i-need-211x150.jpg)