Graphics Card is one of the most important components of a gaming PC or a professional high-performance PC. It packs a huge amount of power and has different components that work altogether for graphics processing. Also, the graphics cards come with different types of connectors for different purposes. Some are for power and some are for connecting display cables and so on. Many users are not aware of the various components and parts of a graphics card, so for them, I am going to explain all the major components and connectors of a graphics card.
Must Read:
Major Components of Graphics Card
Here are the major components that are present in all graphics cards.
GPU
GPU or Graphics Processing Unit is the main component and heart of the graphics card. It is also known as Graphics Processor and does all the processing on your graphics card. Generally, most graphics card comes with only one GPU but there are a few dual GPU graphics cards also. The working of GPU is governed by its architecture which is known as GPU architecture. Different GPU series have different GPU architectures. Also, different GPU manufacturers have their own GPU architecture and layout.
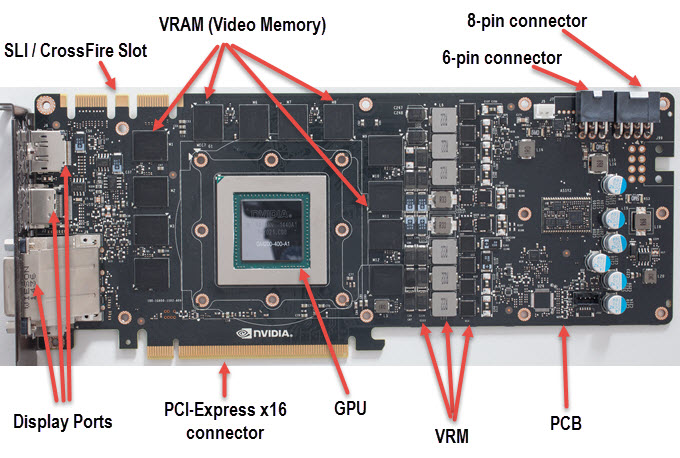
For example, currently, the latest GPU architecture from Nvidia is Pascal and from AMD it is Polaris. There are hundreds and thousands of cores in GPU for parallel processing and multi-tasking. The functionality of these processor cores is governed by GPU architecture. Nvidia calls them CUDA Cores and AMD calls them Stream Processors but technically they are different from each other because of the different GPU architectures involved. Generally newer the GPU architecture, the better the performance of the graphics card, and also it has lower power consumption compared to the older architectures.
VRAM
This is the second most important component of a graphics card. VRAM or Video RAM or Video Memory is the place where all the graphics data and game textures are stored for processing by the GPU. Faster memory can really increase the graphics card performance to a certain level. It is to be noted that memory alone cannot increase the performance in games because if your GPU is weak then you will never have greater performance no matter how fast the RAM is.
There are various types of Video RAM available for graphics cards depending on the speed and bandwidth they offer. Graphics card memory includes DDR3, GDDR5, GDDR5X, HBM, and HBM2 RAM. DDR3 is the oldest and slowest of all and is used mainly in entry-level graphics cards. GDDR5 is the most popular and commonly used VRAM that is used in the budget, mid-range, and high-end graphics cards. GDDR5X is almost twice as fast as GDDR5 and is used in a few top-end graphics cards from Nvidia. Nvidia Titan X, GeForce GTX 1080, and GeForce GTX 1080 Ti use GDDR5X memory. HBM (High Bandwidth Memory) and HBM2 are the most advanced graphics card memories for gaming and VR (Virtual Reality) and are used in high-end graphics cards only. Radeon R9 Fury X and Radeon Pro use HBM memory. HBM memory is faster, requires lesser space on PCB, and has lower power consumption compared to GDDR5 memory. You can read the complete comparison of all these graphics card video memories by going through the link given below.
VRM
VRM or Voltage Regulator Module is the main circuitry that powers the GPU. VRM converts higher voltage from the power supply to lower voltage levels for use in GPU. Generally, it converts 12V to around 1V to 1.5V (approx) which is normally the voltage level at which GPU operates. Along with GPU and VRAM, VRM is also one of the most important components of a graphics card. VRM is also called a Processor Power Module (PPM) or simply Voltage Regulator.
The number of Voltage Regulators on a graphics card varies from card to card. Some graphics cards have a higher number of VRMs compared to others. VRMs can get very hot and sometimes even hotter than GPU and they require good cooling to keep the graphics card from shutting down.
Note: As explained above, VRAM and VRM are completely different components and they should not be confused with each other.
Cooler
Every graphics card comes with a Cooler to keep the temperature of GPU, VRAM, and VRM down to safer levels. Graphics Card coolers can be either active or passive. In active cooling, the cooler has both a heatsink and fan (HSF) whereas in passive cooling the cooler has the only heatsink. Most graphics cards employ an active cooling solution because generally it requires lesser space and provides better cooling especially during overclocking, whereas passive cooling is generally used in entry-level and less powerful GPUs and is totally silent in operation. But there are a few good mid-range graphics cards that also come with a passive cooler or only a heatsink. Also, it is not advisable to overclock your graphics card on a passive cooling solution because it has a limited cooling capability.

The number of fans used in an active cooling solution varies with the graphics card manufacturer. Some of the high-end graphics cards also come with Liquid / Water Cooling or Hybrid Cooling Solution. You can learn more about graphics card cooling solutions by going to the link given below.
Check out: Various Types of Graphics Card Cooling Solutions
PCB
PCB or Printed Circuit Board is the base or board where all the components including GPU, VRAM, VRM, Capacitors, Sensors, etc, and Display Ports are mounted. High-end graphics cards have more components so they require larger PCB compared to mi-range and entry-level graphics cards.
See also: Best Laptops Graphics Cards for Gaming
Major Connectors of Graphics Card
Here are the various connectors that you can find on a graphics card. Some connectors are found in only mid-range to high-end graphics cards and some are present in all graphics cards.
PCI Express x16 Connector
PCI Express x16 Connector is present in all the modern-day graphics cards. It is the only interface through which graphics cards communicate with the motherboard and processor. Older interfaces are PCI and AGP which are outdated and are not used now. PCI Express x16 Connector goes in the PCI Express x16 Slot in the motherboard and it can provide up to 75 Watts of power to the graphics card.
6-Pin & 8-Pin PCI-E Connectors
Graphics cards that have higher power consumption need external power from the PSU through 6-pin or 8-pin connectors. Some cards have only one 6-pin connector, some have one 8-pin connector and high-end cards come with both 6-pin and 8-pin power connectors. There are a few graphics cards too that have two 6-pin or two 8-pin power connectors but they are very rare.
A 6-pin power connector can provide 75 Watt to your graphics cards and an 8-pin connector can provide 150 Watt to the card. Most mid-range graphics cards come with one 6-pin connector and high-end graphics cards come with one 8-pin connector or both 6-pin and 8-pin connector if it has higher power consumption.
Must Read: 6-pin and 8-pin PCIe connectors explained
Display Ports / Connectors
All graphics cards come with display ports for connecting them with your monitor using a display cable. There are different types of display ports or connectors that are VGA, DVI, HDMI, and DisplayPort (DP). VGA is analog technology and supports lower resolution whereas DVI, HDMI, and DP are digital displays and support higher resolutions and picture clarity.
SLI / CrossFire Slot
Multi-GPU compatible graphics cards have SLI Slot or CrossFire Slot on top of the graphics card PCB for running them in multi-GPU or dual GPU setup. The two or more SLI/CrossFire graphics cards are connected using the SLI connector or CrossFire connector. You should know that SLI is Nvidia multi-GPU technology and CrossFire is AMD’s multi-GPU technology.
Have Queries?
Well, here I tried my best to explain everything about graphics card components and their connectors. If you think that something is missing or you have any queries then you can reach me by leaving a comment below.
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through the links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)

![GPU Artifacts while Gaming or Otherwise [Causes and Fixes] GPU Artifacts while Gaming or Otherwise [Causes and Fixes]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/gpu-artifacts-causes-fix-211x150.jpg)
![GPU Crashing Under Load [Causes and Fixes for Nvidia or AMD Cards] GPU Crashing Under Load [Causes and Fixes for Nvidia or AMD Cards]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/gpu-crashing-under-load-211x150.jpg)
very helpful article
Thanks
very good article for begginers .
Excellent article! Well done. I do have a question: do the different monitor connectors receive different priorities? If I have dvi, hdmi and display port, can I tell Windows 7 to use dvi for the primary windows desktop?
What do you mean by primary windows desktop?
What are the small flat fingers on the same side of PCI?
What flat fingers are you referring to?
On left and right side of the PCI, are they guides for inserting into the PCI slot?
Yes