Graphics Card is one of the most important components of a PC, especially in a gaming desktop or workstation. Along with the CPU, Graphics Card is also one of the most powerful and hottest running components of a computer. A graphics card performs millions of operations per second during gaming or running GPU-intensive applications and can get very hot. When we talk about graphics card overheating then most of the time it generally points to the GPU overheating. However, other important graphics card components like VRAM (Video Memory) and VRM can overheat too and may lead to serious issues.
There can be various factors both software and hardware that can cause your graphics card to overheat. In most cases, the overheating is generally caused due to hardware factors but overheating may also occur due to software issues at the operating system level or firmware level. Running graphics cards at very high temperatures is not recommended at all and the issues contributing to overheating should be addressed as soon as possible. So, if your graphics card is overheating and if you want to troubleshoot the cause then here, I am listing down the top causes of graphics card overheating along with the solutions.
What is considered a high GPU temperature?
Graphics card temperature depends on some factors and it varies from one graphics card to another even if they have the same GPU. This is because of the cooler design and performance, factory overclocking (if applicable), ambient temperature and how good is your airflow inside the PC Case. Each component of a graphics card has its rated maximum safe operating temperature and it can vary from one manufacturer to another. However, in general, the maximum safe operating temperature of most GPUs is up to 80°C to 85°C. For VRAM it is up to 90°C and for VRM it is up to 100°C. There can be slight variation in temperatures as some components may be able to operate at slightly higher temperatures but it is better to keep them below the temperatures mentioned here.
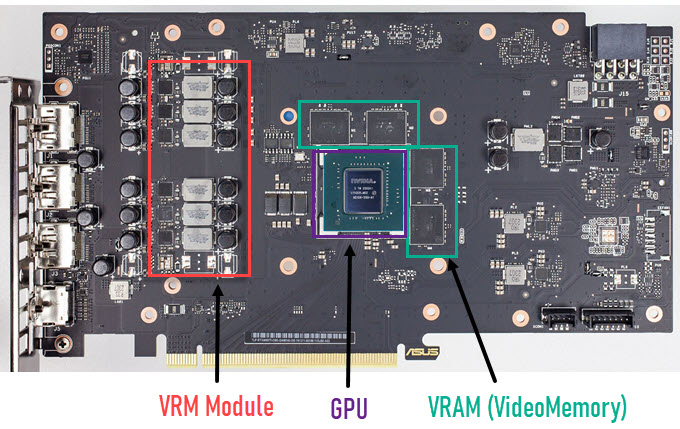
Safe/Ideal Temperatures for GPU, VRAM, and VRM
| Graphics Card Components | Safe/Ideal Maximum Operating Temperature |
| GPU | Under 80°C or 85°C (Ideal 70°C to 75°C) |
| VRAM | Under 90°C (Ideal Under 80°C) |
| VRM (Inductors, Mosfets, Capacitors, etc.) | Under 100°C or 120°C (Ideal Under 90°C) |
If your GPU crosses the safe maximum operating temperature threshold then it throttles down to lower frequencies and delivers lower performance. It is done to prevent the GPU from any damage due to overheating. In some cases, running a GPU at higher temperatures close to its maximum operating temperature can also result in damage to the GPU. Similarly, other critical graphics card components that include VRAM and VRM can also get damaged due to overheating or running at much higher temperatures.
How to Monitor Graphics Card Temperature?
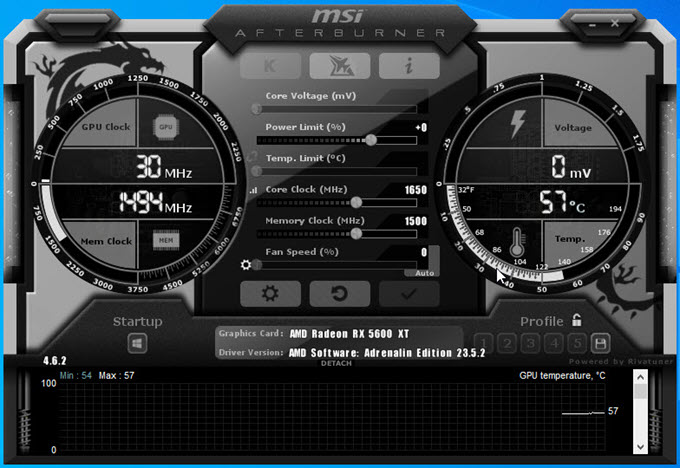
You can monitor graphics card temperature in real-time using official or third-party graphics card software such as MSI Afterburner, GPU-Z, SAPPHIRE TriXX, etc. These software allow real-time monitoring of graphics card GPU, VRM, and CPU temperature. Some of them support OSD (On-screen Display) while other monitors these parameters in the background and record them in log files.
Top Causes & Solutions for Graphics Card Overheating
Below are the top software and hardware causes of graphics card overheating.
Software Causes
Below are the software causes that can contribute to graphics card overheating.
Manual Overclocking
If you have overclocked your graphics card then it will run hotter than normal. Overclocking may result in slightly higher performance or you may gain extra FPS in games but you have to compromise on certain things that include temperature, noise, and overall lifespan of the graphics card components. Overclocking makes your graphics card run at higher clock speeds (GPU & Memory) and it also puts a lot of stress on other components too because of higher temperatures, increased power consumption, and faster processing. Sometimes you may have to increase the power limit and voltage of the GPU to achieve stability during overclocking. The amount of overclocking you can achieve depends on several factors that include the GPU model, cooler size and cooling performance, unlocked power limit, and VRM Phases. So, if you have manually overclocked your graphics card using any graphics card overclocking software and utility then either lower the overclocking or disable it and monitor the temperature again. If your graphics card is still overheating after disabling the overclock (or lowering it) then you have to look for other causes.
Buggy Graphics Drivers
Sometimes buggy graphics card drivers may cause the GPU to overheat. For example, in the past, GeForce 511.65 graphics driver from Nvidia was causing some graphics card models to run at higher temperatures than normal e.g. if a graphics card was running at around 70 – 75 degrees Celsius in games then after installing the GeForce 511.65 driver, the GPU was running at around 85 degree Celsius in same games at same settings. In such situations, the only solution is to roll back to previous drivers until the manufacturer fixes the problem by releasing updated drivers. Here, it is a must to use DDU (Display Driver Uninstaller) for graphics driver uninstallation or removal before installing the older or newer graphics drivers.
Faulty VBIOS / Firmware
A faulty or buggy GPU BIOS or Firmware may also cause overheating of a graphics card due to misconfigured parameters e.g. an unoptimized fan speed curve. It is an issue that can only be rectified by updating your VBIOS or Firmware to the latest one when the manufacturer releases a fix for the problem in the latest version. If you think that your graphics card fans are spinning slowly even at higher GPU loads then you can set a custom fan curve with higher fan speeds to combat overheating of your graphics card. For setting up a custom fan curve, you can either use official or any good third-party graphics card overclocking software or utility. A good recommendation from my side is MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision (for Nvidia Cards only).
Hardware Causes
Below are the main hardware causes that can make your graphics card to overheat.
Faulty Fans
One of the main causes of graphics card overheating is faulty fans. If your graphics card fans are spinning slowly or not spinning at their rated speed then your graphics card’s major components like GPU, VRAM, and VRM will run hotter and may overheat if the graphics card is running at maximum load continuously during gaming or running GPU intensive applications or software. The major cause of fans spinning slowly is because of faulty fans which can be due to worn-out bearings. If your graphics card fans are making squeaking, clicking, or rattling noises then it means either the fan bearing are worn out or they got jammed due to dust. Here, you may lubricate the fan bearing using a light oil e.g. machine oil as a temporary fix but the recommended solution is to replace the faulty fans with new ones. For replacing the GPU fans, you have to find the exact fans with the same size/dimensions, voltage & current rating, and connector type. Below is a detailed guide on how to find and replace graphics card fans.
Related:
Bad PC Case Airflow
Bad airflow in your PC Case can also contribute to overheating of your graphics card and other components inside your PC Case. Bad airflow can occur due to bad configuration of PC Case fans, selection of inferior and improper Case fans, improper placement of AIO CPU Cooler Radiator (if installed), or due to less number of PC Case fans inside the Case. Sometimes, a bad PC Case design can also be the cause of bad airflow and in this case, the only solution is to buy a PC Case with good airflow. Below are some very important articles on how to improve the airflow inside the PC Case.
- PC Case Fans Airflow Guide
- Best Airflow PC Cases
- Best High Airflow PC Case Fans
- Best High Static Pressure PC Fans
High Ambient Temperature
High ambient temperature may also increase your graphics card temperature and other internal PC components. It generally happens during summer time and if you live in a hotter city or town with a much higher temperature in summer then your PC will run hotter. The only solution to this problem is to turn ON the air conditioning when you are gaming or doing heavy intensive work that stresses your graphics card and processor.
Worn-out Thermal paste
Heavy usage and constant running of the graphics card for longer periods may result in the thermal paste losing its effectiveness, especially if the thermal paste is not of good quality. The worn-out thermal paste may become hard over time and its heat conductivity can decrease to significant levels. This problem can be addressed by replacing the thermal paste with a good one like Artic MX4, Thermal Grizzly Kryonaut, Noctua NT-H2, etc. Changing the thermal paste on a graphics card is not a difficult task especially if have you applied thermal paste before on a processor. To change the thermal paste on a GPU, you have to remove the shroud by unscrewing the screws that hold it on the PCB. After that, you have to clean the existing or older thermal paste from the heatsink and GPU using Isopropyl alcohol 99.9% and then apply the new thermal paste on the GPU die.
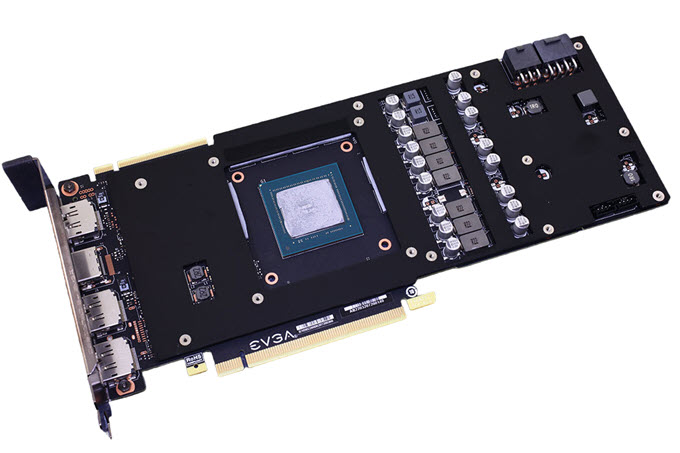
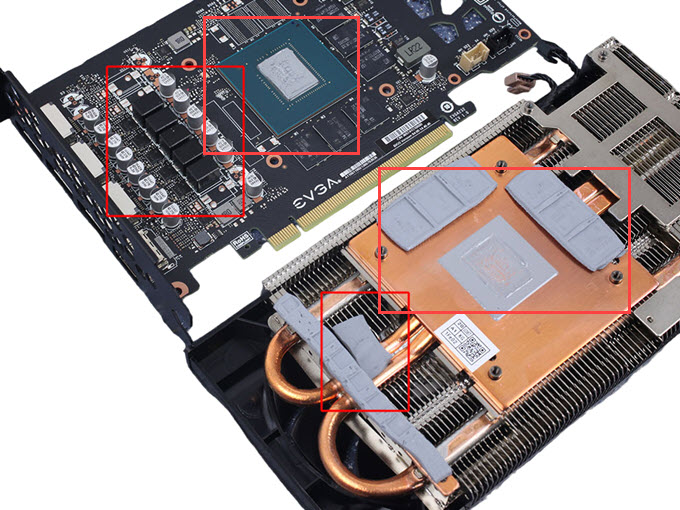
Improper Heatsink contact with GPU, VRM & VRAM
If your graphics card heatsink is not in proper contact with the GPU or there is a small gap between the GPU and the heatsink then it will lead to GPU overheating because of loss of heat transfer from the GPU to the heatsink. This generally happens because of the improper mounting pressure of the heatsink GPU base plate on the GPU either due to manufacturing defect or if you have not applied proper torque to the screws when fitting the heatsink after changing GPU thermal paste, GPU fans, or thermal pads of the VRAM or VRM. If it is a manufacturing defect then you have to contact the manufacturer for a proper solution or RMA the card to get a one that has no issues like this. You may also increase the mounting pressure of the heatsink on the GPU by trying washers of different thicknesses but it is a risky process and should be done only by users who are into small DIY hardware repairs.
Important Note: While changing the thermal pads, do not use too thick thermal pads because if you do then the contact between the GPU and GPU heatsink baseplate will not be proper and this will lead to GPU overheating and crashing. So, always use thermal pads of proper thickness when replacing older thermal pads.
Bad Cooler Design or Underpowered Cooler
A bad or underpowered cooler on a graphics card can also cause overheating of the graphics card during GPU-intensive applications or gaming. To address this issue, you can use expansion slot graphics card coolers that install in the expansion slot of the PC Case below the graphics card. These graphics card fan coolers come with triple fans (80mm or 92mm fans) and they blow air directly on the graphics card shroud to increase airflow and push more air into the heatsink of the card.
Check out Graphics Card Fan Coolers
See also:
- Top Ways to Fix Motherboard and Graphics Card VRM Overheating
- Fix Power Supply Overheating [Symptoms & Solutions]
Need Help?
If your graphics card is still overheating and you need some help regarding it then please leave a comment below, clearly stating all relevant details.
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through the links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)
![How to Find Right Power Supply for Graphics Card [Detailed Guide] How to Find Right Power Supply for Graphics Card [Detailed Guide]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/how-to-find-power-supply-for-graphics-card-211x150.jpg)
![Why does my PC keep Crashing? [Top Causes & Solutions] Why does my PC keep Crashing? [Top Causes & Solutions]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/why-does-my-pc-keep-crashing-211x150.jpg)
![Fix VRM Overheating on Motherboard and Graphics Card [Top Solutions] Fix VRM Overheating on Motherboard and Graphics Card [Top Solutions]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/fix-vrm-overheating-211x150.jpg)