For gaming, whether to upgrade your CPU or GPU first is the most common dilemma faced by many PC users, especially the novice ones who do not have that much experience in the computer hardware field. There are many factors involved in making this decision and you should be fully aware of what you are doing because a wrong decision can end up wasting your hard-earned money and also you won’t be able to achieve the desired performance or result. So, if you are having this confusion that whether you should be upgrading to a GPU or CPU first then need not worry as I am going to clear all your doubts on this matter.
When to Upgrade CPU First
If you are facing a severe CPU bottleneck in the latest games then it is a sign of a weak or underpowered CPU. A CPU bottleneck occurs when your processor is not able to keep up with your graphics card performance. In such a situation, the CPU usage or utilization stays at around 100% but the graphics card usage will be quite lower i.e. much lower than 99% or 100%. When you pair a weak CPU with a relatively powerful graphics card then such a situation can arise and you will face stuttering and lower performance or FPS in games. For example, if you pair dual-core Intel or AMD processor with a relatively newer mid-range graphics card from AMD or Nvidia, or a quad-core processor with a high-end graphics card e.g. pairing Intel Core i5 7600 with Nvidia RTX 2080. The CPU bottleneck is more pronounced in CPU-demanding games having lots of advanced graphics effects such as volumetric lighting, dynamic shadows, reflections, etc.
Factors to consider when upgrading CPU
Upgrading the CPU is a lot trickier because of the various factors involved mentioned below.
CPU Socket Type
The most important thing to look for when upgrading a processor is the CPU Socket type. If your current Socket type is not compatible with the CPU that you have selected for the upgrade then you have to upgrade to a new motherboard and possibly the RAM. For example, if your current CPU uses LGA 775 Socket and you want to upgrade to a CPU that uses LGA 1151 Socket then you have to buy the motherboard that uses LGA 1151 Socket. Moreover, in this case, you have to upgrade to DDR4 RAM as the LGA 775 motherboards support DDR3 RAM while the LGA 1151 motherboards support DDR4 RAM.
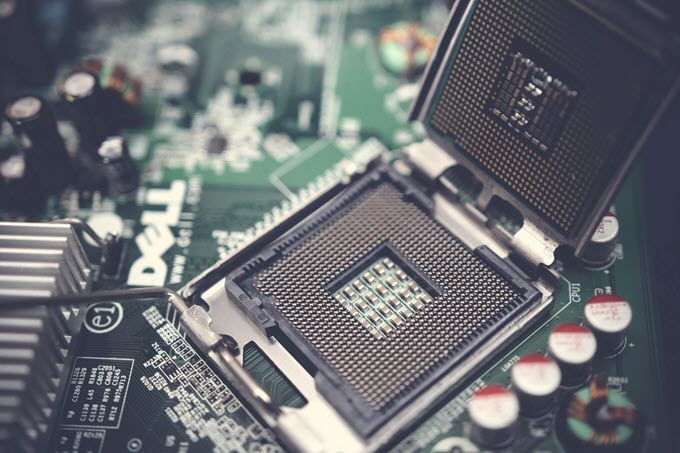
Motherboard & BIOS Compatibility
Even if your CPU and motherboard have the same CPU socket then also it is not guaranteed that they will work with each other because of certain compatibility issues. It means your motherboard and motherboard BIOS should officially support the CPU with the same Socket type. For example, both Intel 6th / 7th generation and Intel 8th / 9th generation processors have LGA 1151 Socket but they cannot function on LGA 1151 Socket designed for a specific CPU series type. It means an Intel 6th / 7th generation processor cannot work on a motherboard designed for Intel 8th / 9th generation processors and vice versa. An Intel 6th / 7th generation processor only supports Intel 2000 series chipset motherboards such as Intel Z270, H270, B250. Similarly, Intel 8th / 9th generation processors support Intel 3000 series chipset motherboards that include Intel Z390, H370, B360, H310.
Another very important factor that comes into play is the BIOS support for the CPU even if the processor series is compatible with the motherboard series. For example, a new processor in the supported series may not work on the supported motherboard series with older BIOS. In this case, you have to update the motherboard’s BIOS so that it can get detected and work without any issues. You can check the processor compatibility with the motherboard you have on the motherboard’s manufacturer website and can also download the latest BIOS from there.
Must Read: How to know what motherboard you have in your PC?
CPU Cooler Compatibility & TDP
Your current CPU Cooler should be compatible with the Socket of the CPU or motherboard you are upgrading to. Also, the CPU Cooler should have sufficient TDP or cooling capacity to cool down your new CPU otherwise you will face CPU overheating and throttling issues which will result in loss of performance and lifespan of your CPU. If your CPU Cooler TDP rating is not enough to support the new CPU then you have to upgrade to a better CPU cooler. If you are upgrading to a high-end CPU then it is better to get an AIO or Liquid CPU Cooler if your budget allows you to and if you are upgrading to a mid-range CPU then a good aftermarket CPU Air cooler should be enough even with some amount of manual overclocking.
Must Read: AIO vs CPU AIR Cooler Comparison
Note: The TDP rating of a CPU Cooler specifies its cooling capacity. The TDP of the CPU Cooler should be more than the TDP of power consumption rating of a CPU. For example, you cannot use a 95W TDP CPU Cooler with a CPU having power consumption or a TDP of 125W.
Check out: How to Find the Right CPU for your Gaming PC
When to Upgrade GPU First
If you have a powerful CPU but a weak, older, or a budget entry-level graphics card then you should upgrade your GPU first. For example, if you have a newer Core i7 or Ryzen 7 processor and a GeForce GT 1030 graphics card then you will be seriously GPU bottlenecked and won’t be able to play the latest AAA games at high graphics settings with 60+ FPS. In this scenario, a viable upgrade would be a GeForce GTX 1660 SUPER or a Radeon RX 5600 XT.
Factors to consider when upgrading GPU
Upgrading to a newer GPU is relatively easier and trouble-free compared to a CPU upgrade because in most cases it does not involve changing your pre-installed components. However, there are some things that you should be aware of when upgrading GPU, which are mentioned below.
PCIe x16 slot
Your motherboard should have a PCIe x16 slot to install the graphics card in your case. Nowadays all graphics cards use a PCIe x16 slot for installation but in older days, the AGP slot or even standard PCI slot was used for discrete graphics cards.
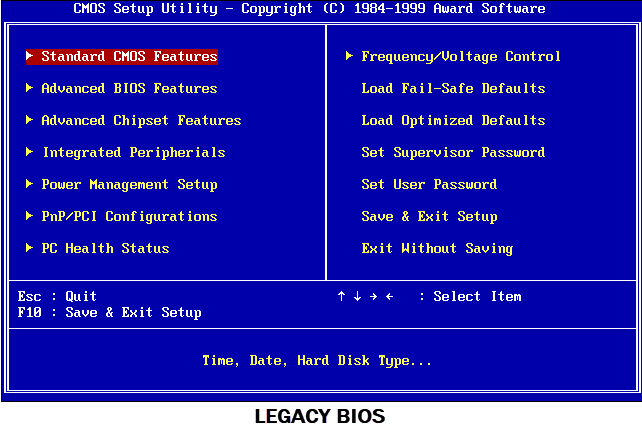
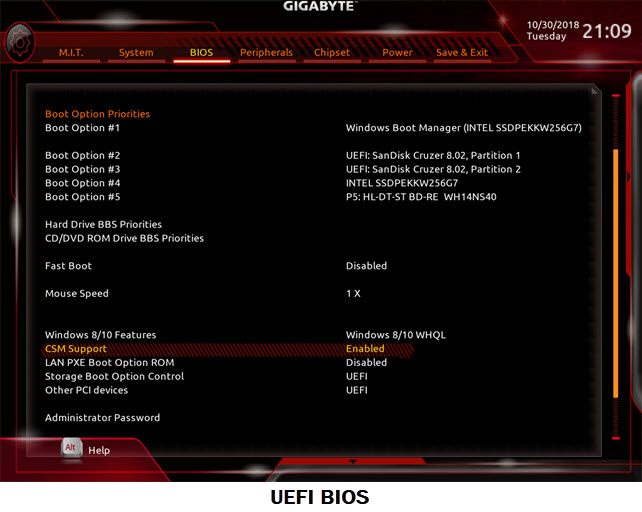
Motherboard BIOS Compatibility
The graphics card you are buying should be able to work on your motherboard and should be supported by your motherboard’s BIOS. Older motherboards that only support Legacy BIOS will not work with modern-day graphics cards that only work with UEFI BIOS. Some modern-day motherboards do support both Legacy and UEFI modes which means they are compatible with almost all graphics cards. So, the motherboard’s BIOS compatibility is a very important factor that comes into play when you are in process of upgrading to a newer graphics card.
Power Supply (PSU)
Your current PSU should be powerful enough to fulfill the power requirements of your new graphics card. If your PSU is underpowered then you may end up burning your power supply and it may cause damage to your other components too. For example, the PSU recommendation for a GeForce GTX 1660 is 450W and if you have a 300W PSU installed in your PC then you will face some serious issues that can be catastrophic in some cases. Also, make sure that your power supply has required 6-pin/8-pin PCIe power connectors that are required by mid-range and above graphics cards.
Must Read: Top PC Power Supply Calculator Tools to Find Right PSU Wattage
PC Case Compatibility
Graphics Card Form Factor is also a very important factor during the GPU upgrade because if your PC case does not have the required clearance for the graphics card model you have selected then you won’t be able to fit it in the PC Case. So, before purchasing a graphics card, do check its physical dimensions and match it with the GPU clearance offered by your PC Case.
- Graphics Card Types Form Factor Types
- Graphics Card Upgrade Guide for Gaming PC
- Graphics Cards Slot Width Explained [Single, Dual, 2.2, 2.3, 2.5, 2.75]
Operating System Support
The graphics card you have selected for an upgrade should be supported by the operating system you are running. Some graphics cards are not supported by Linux, Mac OS, and older Windows operating systems. You won’t be able to find the drivers of the graphics card for a non-supported operating system, so do keep this in mind during the GPU upgrade.
When to Upgrade Both [CPU & GPU]
If you have a pretty outdated processor and a graphics card then you have to upgrade the whole PC if you want to play the latest AAA games at high graphics settings with 60+ frame rates. For example, if you have an Intel Core 2 Duo or AMD FX processor paired with Nvidia GeForce GT 610 or AMD Radeon HD 6450 then you have to upgrade both CPU and GPU which ultimately means upgrading the whole PC itself.
Read also:
Queries?
If you have any doubts regarding the CPU or GPU upgrade then you can ask me your queries in the comment section below.
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through the links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)
![Fix Low GPU Usage in Games [Nvidia & AMD Graphics Cards] Fix Low GPU Usage in Games [Nvidia & AMD Graphics Cards]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/fix-low-gpu-usage-211x150.jpg)
![Fix Stuttering in Games [Causes and Top Solutions] Fix Stuttering in Games [Causes and Top Solutions]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/fix-game-stuttering-211x150.jpg)
![How to Reduce Input Lag in Games [Top Tips & Solutions] How to Reduce Input Lag in Games [Top Tips & Solutions]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/reduce-input-lag-games-211x150.jpg)