High CPU idle temperature is a very frustrating issue that can affect the overall performance of your PC or laptop. High CPU idle temperature means your CPU or processor temperature is significantly higher when you are not working on your PC or there is no application running on your operating system other than the necessary background services or processes. Regardless of the CPU model (excluding high TDP flagship CPUs), if your CPU temperature is idling at around 45 degrees to 50 degrees Celsius (or even higher, i.e., 50 °C, 55 °C or 60 °C), then your CPU is running on the hotter side given that the ambient temperature is lower in your room. Generally, a modern-day CPU from Intel and AMD (mainstream to mid-range) would run about 10 °C to 15 °C hotter than the ambient temperature when idle.
A CPU’s or Processor’s higher idle temperature can pose a serious risk because it can affect the peak CPU temperature and may cause overheating. This results in CPU throttling, leading to performance loss and reducing the CPU’s lifespan. Various factors can cause higher CPU idle temperature, and I will list all of them here, along with proper solutions or fixes.
How to Monitor CPU Idle Temperature?
You can monitor the CPU Idle temperature using good hardware monitoring tools like Core Temp, HWiNFO, or HWMonitor.
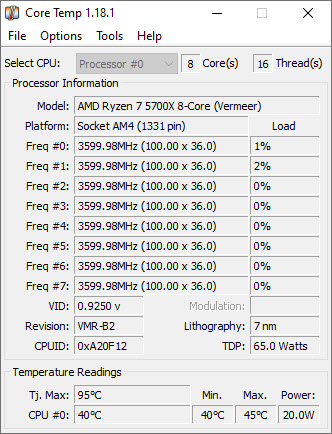
Top Causes and Solutions for CPU High Idle Temperature
Below are the main factors causing the high idle temperature of your CPU. All these factors are grouped under three scenarios or cases so that you can quickly figure out the root cause.
Scenario 1: No Change in CPU or CPU Cooler
If you haven’t changed your CPU or CPU cooler but are suddenly getting higher CPU idle temperatures, the following factors may have contributed to this problem.
1.1 High Ambient Temperature
High Ambient Temperature is one of the most common reasons that can cause the idle temperature of the CPU to rise. If your ambient temperature rises significantly in summer or your room ambient temperature increases for any other reason, your CPU idle temperature will be higher. Generally, the idle temperature of a CPU on a decent CPU Cooler is 7 to 20 degrees Celsius higher than the ambient temperature. For example, if your room ambient temperature is 26 degrees Celsius, then your CPU temperature can be around 33 to 40 degrees Celsius, depending on the CPU and CPU Cooler you are having. Laptop CPUs have higher idle temperatures because of the limited cooling design, and their CPU idle temperature can be up to 25 degrees Celsius higher than the ambient temperature. To solve this problem of high ambient temperature, you can decrease the temperature of your room by switching on air conditioning (AC) or improve the CPU Cooler’s performance by adding an extra fan to the CPU Cooler heatsink.
1.2 Overclocking / Overvolting
If you have overclocked your CPU or Processor, you will have higher idle temperatures, especially when you have increased the CPU voltage to provide stability during overclocking. Here, you can either remove the overclocking or upgrade your CPU Cooler (preferably AIO Liquid Cooler) to get the idle temperatures down to your liking.
1.3 Poor Airflow Inside PC Case
Poor airflow inside your PC Case is another major cause of high idle CPU temperature. To increase or improve your PC Case airflow, you can add extra Case fans to your PC Case in proper orientation and direction. If you have a small form factor PC Case, you can add slim PC Case fans or replace the existing fans with high-performance static pressure and airflow fans. Below is a definite guide on improving PC Case airflow.
1.4 Worn-out Thermal Paste
Worn-out thermal paste can also cause high CPU idle temperature. Thermal paste performance degrades over time, and the cheap ones get hardened or thicker over the years and cause higher CPU temperatures. It is advisable to replace thermal paste on your CPU every five years, mainly if stock thermal paste is applied to the CPU. A good thermal paste can last up to 10 years or more, depending on your computer usage and CPU temperatures. Below is a comprehensive post on the best thermal pastes you can buy for your CPU or GPU.
1.5 Malware or Malicious Programs
A malware or malicious program continuously running in the background can also increase the CPU idle temperature. These malicious programs cause CPU usage to spike up and thus cause CPU idle temperature to rise. In Windows Task Manager, you can check which programs or processes are utilizing the CPU continuously. You can use good anti-malware and antivirus software like ESET MOD32 Antivirus and Malwarebytes anti-malware software to remove these malware and viruses. You must also uninstall any unknown or malicious program by going to the Control Panel->Program and Features in Windows.
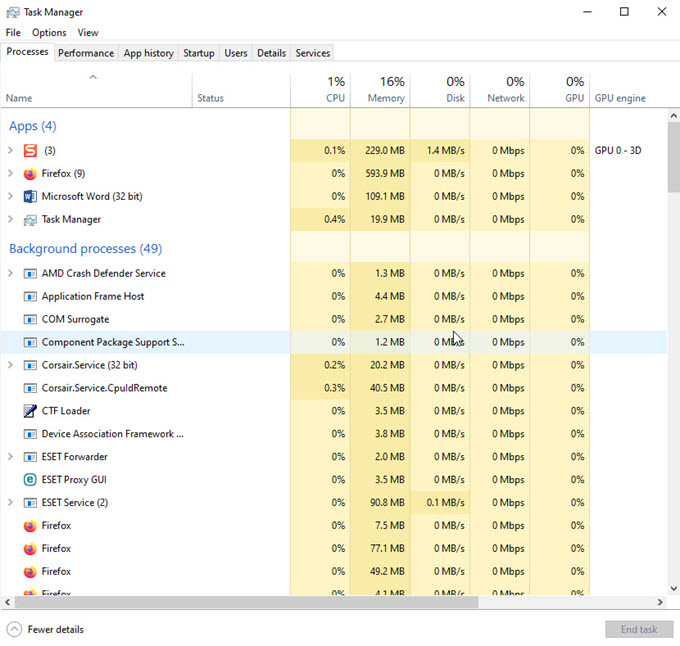
1.6 Dust Build Up on Heatsink and Fan
Over time, accumulation of dust on the heatsink/radiator and fan of the CPU Cooler can lead to a higher idle temperature of your CPU. So, if you haven’t cleaned your CPU Cooler heatsink and fan for a long time, you should clean your CPU Cooler to reduce the CPU idle temperature and improve its cooling performance. Eliminating dust also makes the CPU Cooler run quieter than when it was covered in dust. You can use an electric duster or blower and a soft brush to remove the dust from the heatsink and fan.
1.7 Faulty Software/Firmware or Sensor
In extremely rare cases, a faulty sensor or bug relating to the temperature sensor may also report inaccurate temperature readings. The firmware issue related to the sensor can be fixed by updating the BIOS, but a hardware issue related to the sensor is irreparable. To measure CPU temperature, you should use good and reliable hardware monitoring software, as mentioned above.
1.8 AIO Silent Fan Profile
If your AIO Liquid CPU Cooler is running in silent or quiet profile mode, then you will have higher CPU idle temperatures. Every AIO Liquid CPU Cooler has its proprietary software, which allows you to control fan speed, set pre-defined cooling modes or profiles, and monitor CPU temperature, coolant temperature, fan speed, etc. You can switch from a silent/quiet profile to a balanced or standard profile for better CPU temperatures (both idle and peak).
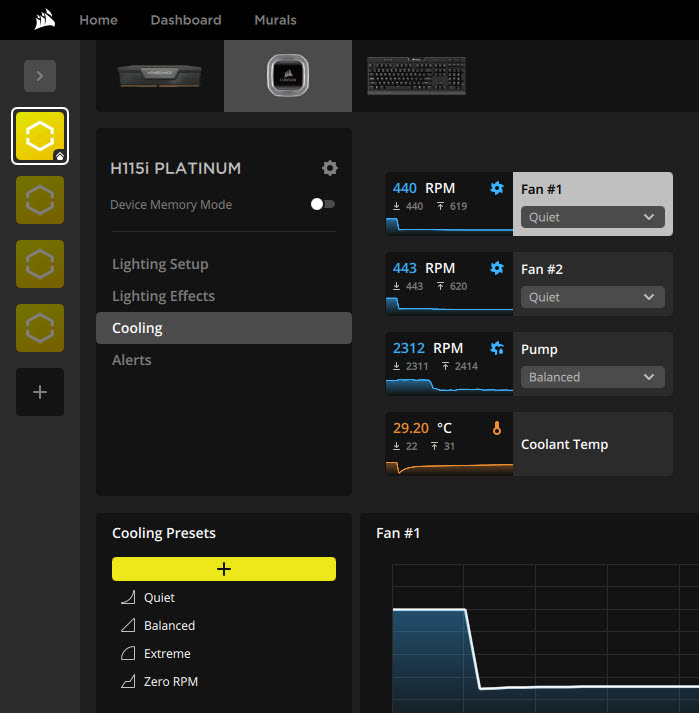
1.9 AIO Faulty Pump or Pump connector not plugged in
A faulty AIO Liquid CPU Cooler pump or if the pump is not running or running at low speed can result in higher CPU idle temperatures. Also, you must ensure that the AIO pump connector is plugged into the motherboard and the pump is running. Monitor the AIO pump speed; if its RPM is too low, you may have a faulty pump.
Scenario 2: When installing a new CPU
If you have installed a new CPU or Processor and are experiencing high idle temperature, the factors mentioned below may be the root cause of this issue.
2.1 Underpowered CPU Cooler
If you have installed a new CPU with a higher TDP than your CPU Cooler is designed to handle then you will have higher idle and peak CPU temperatures. For example, if you have a CPU Cooler that can handle CPUs up to 75W TDP and have bought a new CPU with 105W TDP then you will have higher CPU temperatures (both idle and peak). To fix this issue, you have to get a new CPU Cooler that can handle higher TDP processors or CPUs.
2.2 Improper Mounting of CPU Cooler
After replacing your CPU, if you have not tightened the CPU Cooler mounting screws properly, then you will face higher CPU idle temperatures. The four screws of the CPU Cooler should be tightened in a cross pattern and torqued correctly so that the CPU base plate makes proper contact with the CPU’s integrated heat spreader (IHS). To make sure screws are torqued correctly, you have to tighten the screws to the point where a decent amount of resistance is felt. You should tighten the screws with a light hand because overtightening can cause damage to your motherboard, CPU, or CPU Cooler.
Scenario 3: When installing a new CPU Cooler
If you bought a new CPU Cooler for your Processor and are still getting high idle temperatures afterward, it could be due to the reasons below.
3.1 Improper Mounting of CPU Cooler
Improper mounting of the CPU Cooler and not tightening the CPU Cooler screws properly can result in higher CPU idle temperatures. I have discussed this point thoroughly above in Scenario 2.
3.2 Not Removing Plastic Film Covering
Almost all CPU Coolers come with a thin plastic film on their base to prevent corrosion, scratches, or damage. If you have forgotten to peel off this plastic film from the CPU Cooler base, you will have high idle and peak CPU temperatures. So, check and make sure that you have not made this mistake.

Additional Measures to Decrease CPU Idle Temperature
Here are some extra measures to decrease your CPU idle temperature to your liking.
Adding Extra Fan to Heatsink
If you use a CPU Air Cooler, you can add an extra fan to the heatsink in pull configuration, given that your CPU Cooler supports an additional fan. This will enhance the airflow, and you may see a drop in CPU Idle temperature by a few degrees.
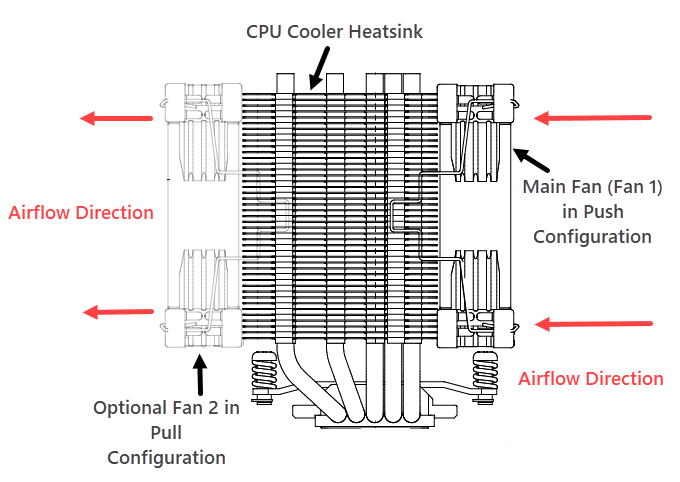
Upgrade CPU Cooler Fans
You can upgrade your CPU Cooler fans to better ones for higher cooling performance. You can replace the stock fans of your CPU Air Cooler or AIO Liquid CPU Cooler with fans having higher static pressure (air pressure) and airflow.
Upgrade CPU Cooler
You can upgrade to a better CPU Cooler if you want lower CPU temperatures at idle and peak CPU usage. You can get to a dual tower CPU Air Cooler or a good AIO Liquid CPU Cooler for better cooling performance.
- Best Dual Tower CPU Coolers
- Best 360mm AIO Liquid CPU Coolers
- Best 280mm AIO Liquid CPU Coolers
- Best 240mm AIO Liquid CPU Coolers
Fan Speed Curve Adjustment
If you have a modern-day motherboard with UEFI BIOS, you can customize the CPU Fan Speed Curve in the BIOS to your requirements. The settings for the fan speed curve can be different for different motherboards depending on the motherboard manufacturer and motherboard model.
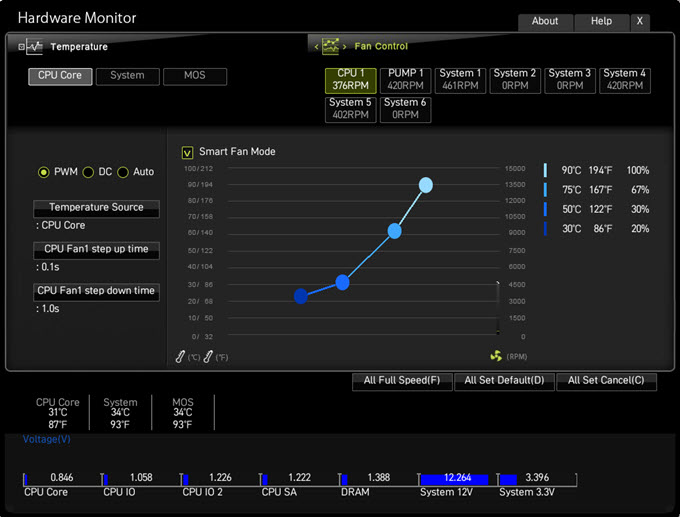
If you do not have the CPU fan speed curve adjustment setting in your BIOS or are not comfortable making changes in the BIOS, then there are some excellent third-party CPU fan speed software that allows you to tweak or change the fan speed of the CPU from the Windows Operating System. One of the most popular fan speed software for Windows is SpeedFan. Another excellent fan speed control software is Fan Control. You can download these fan speed control software for free from the links below.
SpeedFan
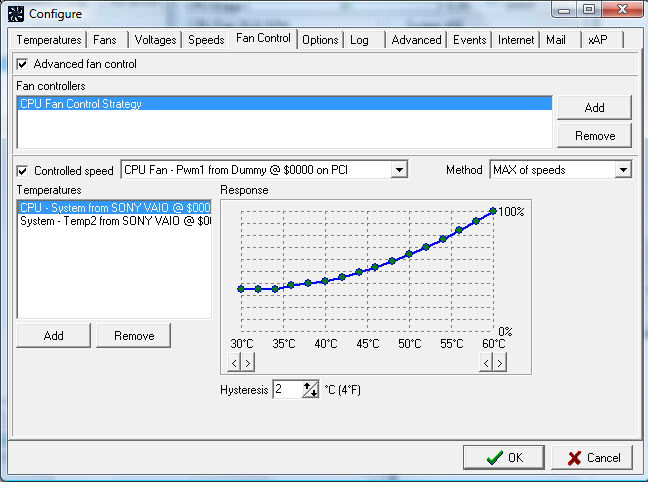
Fan Control
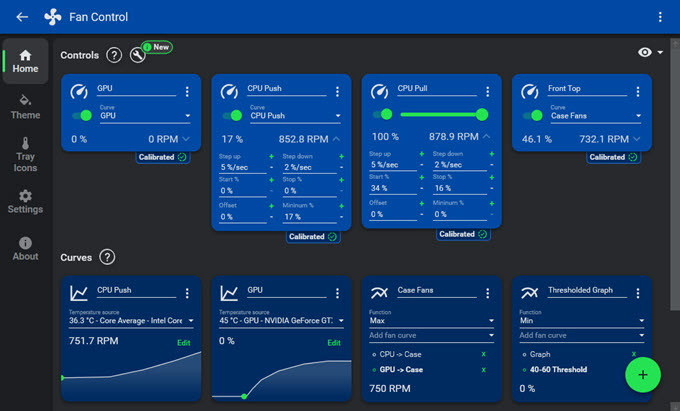
Undervolting the CPU
It is a very advanced measure or process for making your CPU run a little cooler. I would not recommend undervolting your CPU for PC or Desktop users because far better measures are available (mentioned above) to reduce your CPU Idle temperature. CPU Undervolting can be considered for laptop CPUs because limited options exist to decrease your laptop’s CPU temperature. CPU undervolting can be done either in the BIOS or operating system. If your BIOS does not have an undervolting option, you can undervolt the CPU in Windows OS using tools like ThrottleStop for Intel Processors and AMD Ryzen Master for AMD Processors.
Important Note: CPU Undervolting can result in lower performance. Also, if it is not done right, i.e., lowering the voltage too much, you may face stability issues and BSOD (Blue Screen of Death).
See also:
Need More Help?
If you need more help with your CPU’s high idle temperature, please post your queries in the comment section below, providing all relevant details.
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through the links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)
![Calculate SSD Lifespan in Years [Know How Long it will Last] Calculate SSD Lifespan in Years [Know How Long it will Last]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/ssd-lifespan-calculate-211x150.jpg)
![Fix Key Chatter in Mechanical Keyboards [Working Best Solution] Fix Key Chatter in Mechanical Keyboards [Working Best Solution]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/fix-key-chatter-mechanical-keyboard-211x150.jpg)
![Fix PSU Overheating [Power Supply Overheating Symptoms & Solutions] Fix PSU Overheating [Power Supply Overheating Symptoms & Solutions]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/fix-power-supply-overheating-211x150.jpg)