RAM Compatibility is one of the common problems faced by users when upgrading computer RAM or even when building a new PC. Selecting the right RAM is crucial for the proper working of your PC or laptop because a slight amount of carelessness can result in compatibility issues and other problems that could be very frustrating. The major RAM issues include Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), reduced performance, frequent crashing, restarts, and boot issues. So, if you want to know how to check RAM compatibility with your current computer (PC or laptop) then here I am going to present an informative guide on it. If you keep the below-mentioned points in mind then you will never have to face any RAM compatibility issues in the future with your PC or laptop.
How to Check RAM Compatibility?
Below are the various parameters and points that you should be aware of to find the right RAM for your PC or Laptop.
RAM Type
If you don’t know what RAM your motherboard and CPU support then the first task is to know the RAM type supported by your computer. By identifying the correct RAM type that is installed or supported by your computer, you can move to the next parameters that include RAM speed, timings, capacity, and brand. For identifying the RAM supported by your computer, you can use CPU-Z which is a small utility or software that gathers the information about the processor, motherboard, and memory installed in your computer. To check the RAM type, run the CPU-Z software and then go to the Memory section or tab. Here, in the General section, you can see the Type field that lists your RAM type. Here in the example below, you can see the RAM type is DDR4 which means the motherboard will only support DDR4 type RAM and you cannot install DDR3, DDR2, or any other RAM type on this motherboard.
You can also check the RAM Type information using the HWiNFO, a very good and one of the best system information and monitoring software that gives much more detailed information than CPU-Z. To view the RAM Type information, launch the software and in the System Summary window, look for the Memory section where you will get all the necessary details about your RAM.
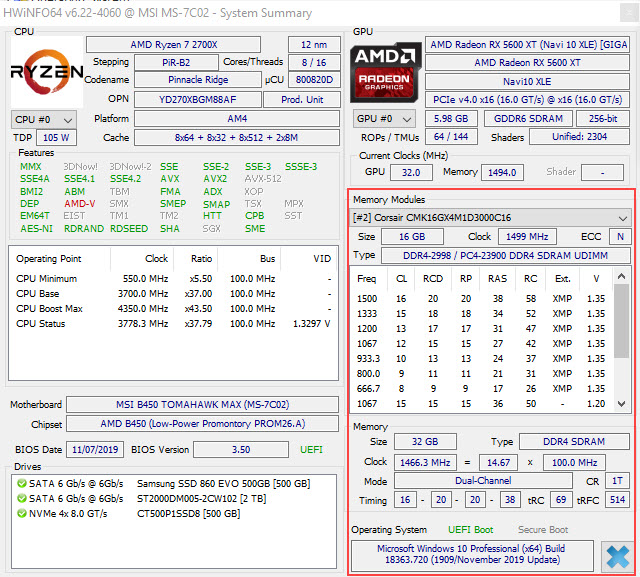
RAM Speed
Memory speed is one of the most important parameters to consider when you are upgrading RAM either by adding extra modules or upgrading all the modules by replacing the older ones. The RAM clock frequency is specified in MHz (Megahertz) and the effective memory speed is specified in MT/s (Mega Transfers per Second). However, in casual or non-formally most of the users and websites use MHz for listing memory speed. You can easily find out the RAM speed from its name which is specified in the format DDRX-Y. Here DDR stands for Double Data Rate, X is the DDR generation and Y is the RAM speed. For example, in DDR4-3000, the RAM type is DDR4 and the speed of the RAM is 3000 MT/s or 3000 MHz (commonly specified). To know the speed of the installed RAM, run the HWiNFO software and then on the left-hand side, expand the Memory list and then click on the memory slot or Row section. Now on the right-hand side, click on the Memory Speed section where you can view your RAM clock frequency and speed. In the below example, the RAM is DDR4-2998 which means it is a DDR4 RAM having a speed of 3000 MHz. Here, you can also see PC4-23900 which is the industry name for DDR4 3000 MHz RAM and the number 23900 denotes its bandwidth which is measured in MB/s.
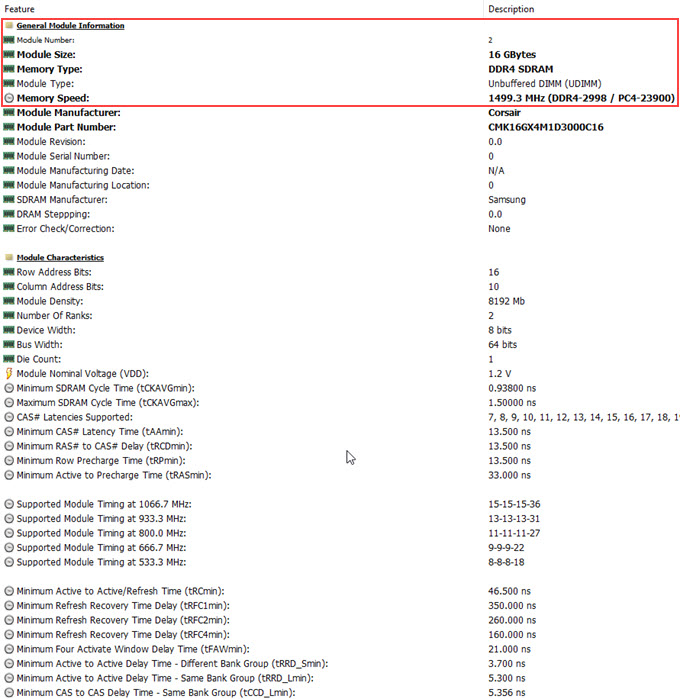
Note: In the above figure, you can also see the Memory Speed as 1499.3 MHz which is the base clock or base speed. You must know that for DDR RAM, the effective memory speed gets doubled. So, here the effective memory speed becomes 1499 x 2 which equals 3000 MHz or MT/s.
If you are upgrading all the RAM modules (including older ones) to a higher speed then you should first have to know the maximum RAM speed and capacity supported by your motherboard. You can find out this information in the technical specifications section of your motherboard model on your motherboard’s manufacturer’s website. Below, you can see the maximum RAM speed and capacity supported by the MSI B450 Tomahawk Max motherboard.

When doing RAM upgrade, if you are only adding extra RAM modules or modules to vacant memory slots then it is better to stick with the memory speed that the older installed RAM has because even if you add a higher speed RAM module then also it will run at the speed of the installed RAM (lower speed one). It is because if you mix memory modules of different speeds then all the memory modules will run at the speed of your slowest module. For example, if you have 8GB DDR4-2666 memory installed on your PC and add an 8GB DDR4-3000 module to it then all RAM modules will run at 2666 MHz speed only. On the other side, if you are upgrading RAM to a higher speed by replacing the older ones then you should not get the RAM that has a speed higher than your motherboard supports otherwise the RAM will run at the highest speed that your motherboard can support. For example, if your motherboard can support only DDR4 3000 MHz RAM but you have installed DDR4 3200 MHz RAM then the RAM will run at 3000 MHz only.
RAM Latency & Timings
Like RAM speed, RAM timings or latency are also very parameters to look for when you upgrade RAM. Memory Timings can be a little bit difficult to understand because of the complexity and technicality associated with them. To understand them in detail, you may have to learn about memory module structure and components present in them. However, here I am going to make it simple for you to understand the basics of memory timings or latencies. In general, Latency is the measure of delay when a command is passed from one body and is received by the target body. The lower the latency, the faster will be the response and the processing of data will begin early compared to the one with higher latency. Memory timings are set of various latencies that occur in the memory module for processing the data. In a DDR RAM, memory timings consist of four parameters or latencies that include CAS Latency (CL), Row Column Delay (tRCD), Row Precharge Time (tRP), and Row Active Time (tRAS). They are commonly written as a set of four numbers separated with hyphens, e.g. 15-17-17-35.
CAS Latency (CL) – This is the time it takes for a memory module to have data ready upon request of the memory controller.
Row Column Delay (tRCD) – The time it takes to read memory after the memory is ready.
Row Precharge Time (tRP) – The time it takes for the memory to have a new row ready for using data.
Row Active Time (tRAS) – Minimum time required for a row to be active to ensure data can be accessed from it.
The most common and widely recognized timing is CAS Latency (CL) which is considered the main parameter to judge the RAM latency. You may also find it written in the RAM name or model number e.g. In Corsair Vengeance LPX 16GB (2 x 8GB) DDR4 DRAM 3000MHz C15 Memory Kit, the C15 specifies the CAS latency of 15. You can also find the CAS Latency value in the specifications section of the memory module.
When upgrading RAM, it is better to get the RAM module with the same memory timings as the older one has. RAM with different memory timings can work together but the memory timings will be set to the module having the loose timings i.e. having higher values for memory timings. For example. If you have a currently running DDR4 3000 MHz RAM module with memory timings as 15-17-17-35 and you add a DDR4 3200 MHz RAM module with 16-18-18-36 timings then all RAM modules will run at 16-18-18-36 memory timings and the RAM speed will be set at 3000 MHz only.
To check the supported RAM Timings of your memory module, run CPU-Z and then go to the SPD tab where you can get the details of your RAM timings at different speeds.
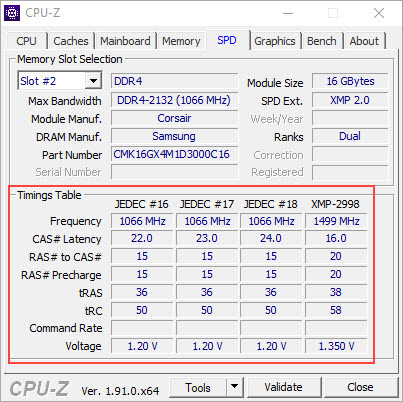
Note: The term loose timing for RAM means higher values of RAM timings and tight memory timing means lower values of RAM timings. For example, 15-17-17-35 RAM timings are tight in comparison to RAM with timing values of 16-18-18-36.
RAM Size & Capacity
RAM modules of different sizes or capacities can work together without any issues but it will not be an optimal setup for dual-channel mode configuration. The dual-channel mode may work with RAM modules of different capacities but it will not be optimal because only the matching capacity of the RAM will run in dual channel mode and the remaining will be operating in a single-channel model. For example, if you have a 4GB RAM module installed and you add an 8GB module then only the 4GB RAM from each pair will run in a dual channel and the remaining 4GB of the 8GB one will run in a single-channel mode. So, if you want to take full advantage of dual-channel mode and want maximum stability then it is better to get a RAM module of the same capacity.
RAM Manufacturer or Brand
RAM modules from different manufacturers or brands can work together without any issues given that they are from reputed brands. However, in a few cases, RAM modules from different brands may not work that well and can cause stability issues resulting in BSOD, crashes, or system restarts. Also, never buy unbranded and refurbished RAM because they are more likely to cause problems in the future and you will end up wasting your money and time.
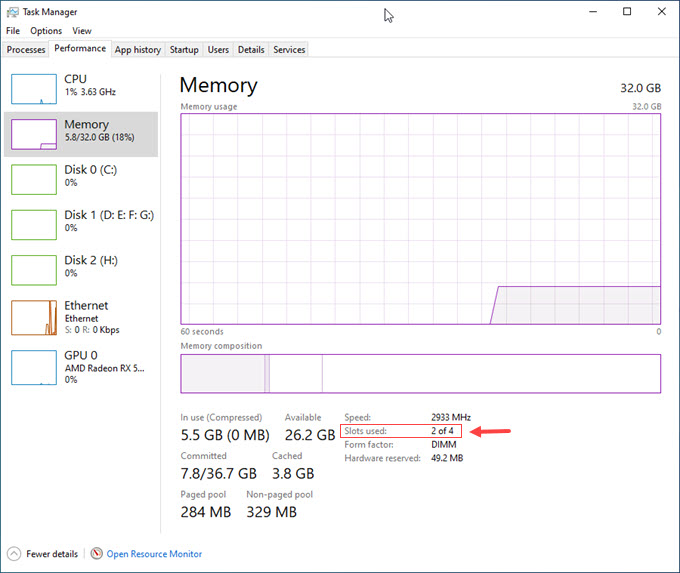
How to find out the total number of RAM slots in your computer?
You can find the number of RAM slots in your PC by opening up the case side panel and looking at the RAM slots present along the sides of the processor. If you do not wish to open the PC case or laptop panel then you can look at this information on the motherboard’s manufacturer website by searching for your motherboard model or in the task manager in Windows 10 by clicking the Memory section in the Performance tab of the Task Manager.
Issues on Mixing and Matching RAM [Is it safe]
Well, mixing and matching RAM modules do work most of the time without any issues. However, in some cases mixing RAM modules with different speeds and latencies may cause issues such as Blue Screen of Death (BSOD). So, if you are upgrading RAM then always try to get exactly the same RAM module i.e. with the same speed, latency, and brand. In some cases, especially where your pre-built PC or laptop comes with OEM RAM installed then it is not possible to get the same OEM RAM module. In such a scenario, get the RAM with the same speed and latency as the original RAM installed in your computer.
Read also:
- How much RAM do you need for Gaming in 2022?
- Top Tips & Tricks to Lower RAM Usage in Windows
- How Much Video Memory (VRAM) Do you need for Gaming?
Queries?
If you have any queries regarding RAM compatibility then you can ask me them in the comment section below.
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through the links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)
![How to Increase Graphics Card Performance [Top Tips & Tricks] How to Increase Graphics Card Performance [Top Tips & Tricks]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/increase-graphics-card-performance-211x150.jpg)


Hi there,
i don’t actually know how to start it, but i am an input lag sufferer from 2020 (from the moment when i bought a new pc). i’d like to to talk with you about RAM, GPU and CPU components before i replace them.
my hardware:
MSI RTX 2060 Ventus 6g OC
HyperX Fury Black 16gb (2 sticks, 2666MHz in total)
MSI B560
i5-10400F
I have 2 psu’s but im using an older one (500W, and i see no difference of input lag at all)
So, the first thing i want to ask – is input lag may be caused by faulty RAM/GPU? And how do i test them both because everything seem to be working fine, but theres still one thing that gives me big suspicions about my components – low gpu and cpu usage in all games. I also want to state that it is not caused by mice or monitor because i’ve replaced them both for multiple times.
Please check out these articles below if you haven’t already.
https://graphicscardhub.com/low-gpu-usage/
https://graphicscardhub.com/reduce-input-lag-gaming/
I did.