GPU is the heart of the graphics card and its working is defined by its architecture, which is called GPU architecture. Each graphics card family has its own GPU architecture and every new family or series of graphics cards comes with a more advanced and powerful GPU architecture.
Every GPU manufacturer designs its own GPU architecture and GPU architectures of graphics cards from Nvidia and AMD are totally different in working, operation and naming. Examples of Nvidia GPU architectures are Fermi, Kepler, Pascal, Volta, and Turing whereas from AMD we have GCN (1.0, 2.0, 3.0), Polaris (GCN 4.0), and Vega. Also, two GPU architectures from the same GPU manufacturer are different in working, efficiency, and performance e.g. Fermi is different from Kepler, Pascal is different from Kelper, and so on. But here I am going to make a comparison of Nvidia’s three modern GPU architectures, which are Pascal, Volta, and Turing based on their specifications, performance, usage & applications in the graphics industry.
Pascal GPU Architecture
Pascal is one of the most popular GPU architectures from Nvidia and the successor of Maxwell GPU architecture. The GeForce 10 series and Quadro P series graphics cards are built on the Pascal GPU architecture. Pascal GPUs are built on the 16nm / 14nm fabrication process and use CUDA Cores as their main pixel processing units and for Rasterization. GeForce GTX 1050, GTX 1050 Ti, and GT 1030 are built on 14nm FinFET technology while others are built on the 16nmm technology process. Pascal GPU architecture brings significant improvements over the older architectures in terms of performance, power consumption (TDP), and heat generation.

Pascal GPU architecture supports GDDR5, GDDR5X, and HBM2 memory. Only a higher-end workstation graphics card, Nvidia Quadro GP100 comes with high bandwidth HBM2 memory. Nvidia Pascal GPU architecture supports DirectX 12, OpenGL 4.6, Vulkan, OpenCL, SLI (for high-end GeForce cards), NVLink (for top workstation GPUs only), NVENC, G-Sync, GPU Boost 3.0, DisplayPort 1.4, HDMI 2.0b, CUDA Compute Capability 6.0 / 6.1 and is VR Ready. Pascal-based GPUs can also be found in Notebooks or Laptops.
Must Read: GDDR5 vs GDDR5X vs HBM2 vs GDDR6 Comparison
Volta GPU Architecture
Volta is the successor of Pascal GPU architecture and is built on the 12nm fabrication process. It supports high-speed and high-bandwidth HBM2 memory. Volta architecture is only designed to cater to workstation and datacenter needs. At present, there are no gaming graphics cards that use Volta architecture. This GPU architecture is powered by CUDA Cores and Tensor Cores. The Tensor Cores are used for Artificial Intelligence (AI), Deep Learning, Machine learning, and Complex arithmetic calculations and provide an over 5X increase in performance compared to the Nvidia Pascal architecture.

The graphics cards that use Volta GPU architecture include Nvidia Titan V, Nvidia Titan V CEO Edition, and Nvidia Quadro GV100. Volta architecture supports NVLink 2.0 technology which is much faster than the previous NVLink and allows much higher data transfer rates of 25 Gbit/s per data lane per direction. We may be able to see more graphics cards using Volta architecture but I think it would be only in the workstation graphics cards category.
Check out: Volta vs Pascal GPU Architecture Comparison
Turing GPU Architecture
Turing is the successor of Volta GPU architecture. It is one of the most advanced GPU architectures ever made. Turing GPUs are built on the 12nm FinFET manufacturing process and support GDDR6 memory which operates at a very high speed and can achieve much higher bandwidth compared to the previous GDDR5X and GDDR5 memories. This advanced GPU architecture comes with CUDA Cores, Tensor Cores, and RT Cores. Turing is the first GPU architecture to support Real-Time Ray Tracing for creating lifelike lighting, shadows, reflections, refractions, and other advanced lighting effects. This Real-Time Ray Tracing is handled by RT Cores and its performance is evaluated in a new metric called Giga Rays per second.
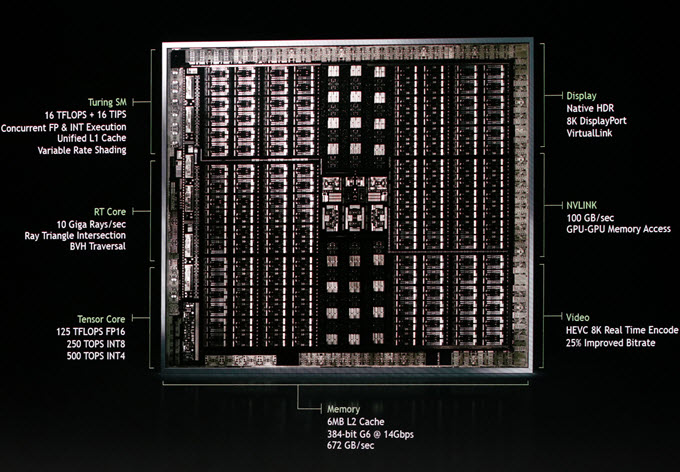
Tensor Cores in Turing GPUs are designed especially for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Deep Learning for performing various types of complex calculations. It is also used for a technique called Deep Learning Super-Sampling (DLSS) or (Deep learning anti-aliasing) for smoothening out edges in games and for denoising, resolution scaling, and video re-timing.
CUDA Cores are used for standard Pixel-based processing tasks or Rasterization, but in Turing, they feature a new streaming multiprocessor (SM) architecture that supports up to 16 trillion floating point operations in parallel with 16 trillion integer operations per second. This can now allow Developers to create complex simulations, such as particles or fluid dynamics for scientific visualization, virtual environments, and special effects. According to Nvidia, Turing GPUs provide up to 6X performance over the Pascal-based GPUs.
There are both workstation and gaming graphics cards based on the Turing GPU architecture. Turing Workstation Graphics Cards include Quadro RTX 8000, Quadro RTX 6000, Quadro RTX 5000, and Gaming Graphics Cards consist of GeForce RTX 20 series that include GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, RTX 2080, RTX 2070, and also the mighty Nvidia TITAN RTX. Turing supports a multi-GPU setup for both Quadro RTX and GeForce RTX graphics cards using NVLink for doubling or tripling their computational performance. GeForce RTX graphics cards also support VirtualLink via a USB Type-C connector for connecting VR Headsets to a USB Type-C port for an amazing VR experience. On the other hand, Quadro RTX GPUs are capable of processing 8K videos in real-time which shows the power of this new architecture.
Update: GTX 16 series Turing graphics cards do not come with RT Cores and Tensor Cores. They include GTX 1660 Ti, GTX 1660.
Pascal vs Volta vs Turing Comparison
A quick and brief comparison of Pascal, Volta, and Turing GPU architectures from Nvidia.
| GPU Architecture -> | Pascal | Volta | Turing |
| GPU Manufacturer | Nvidia | Nvidia | Nvidia |
| Fabrication Process | 14nm / 16nm | 12nm | 12nm |
| CUDA Cores | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Tensor Cores | NA | Yes | Yes |
| RT Cores | NA | NA | Yes |
| Memory support | DDR4, GDDR5, GDDR5X, HBM2 | HBM2 | GDDR6 |
| VR Ready | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| VirtualLink (USB Type-C) | NA | NA | Yes |
| Multi-GPU support | Yes (in high-end cards), SLI and NVLink | NVLink 2 | NVLink 2 / NVLink SLI |
| Graphics Cards | GeForce 10 series, Nvidia Titan X, Nvidia Titan Xp, Quadro P series workstation graphics cards, Quadro GP100 | Nvidia Titan V, Quadro GV100 | Quadro RTX 8000, Quadro RTX 6000, Quadro RTX 5000 / RTX series graphics cards |
| Applications | Gaming, Workstation | Artificial Intelligence (AI), Workstation, Datacenter | Artificial Intelligence (AI), Workstation, Gaming |
See also:
Final Thoughts
Well, it is no denying the fact that Turing is the most advanced GPU architecture and is leading ahead of Pascal and Volta in terms of technology. Turing is more of a multi-purpose GPU architecture that can perform all three things at the same time i.e. Pixel Processing, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Real-Time Ray Tracing. Pascal is a very long-lived and successful GPU architecture but now it has been showing its age because of a lack of AI and Ray Tracing advanced functionalities. Volta is really a question mark for us because there are only a couple of graphics cards from it up till now and according to me it has been completely replaced by the newer and better Turing GPU architecture. The future of graphics definitely lies with the Turing architecture as the previous generation architectures fade out slowly. If you have anything to say then please leave a comment below.
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through the links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)
![AIO Fans Intake or Exhaust? [Ideal AIO Radiator Mounting Positions] AIO Fans Intake or Exhaust? [Ideal AIO Radiator Mounting Positions]](https://graphicscardhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/aio-radiator-fans-intake-or-exhaust-211x150.jpg)


Always giving great information. always well written. thanks
You are most welcome charles.
Good explanation. Thanks
Thank you for taking the time to write this article. I do have a question that you might be able to answer. Currently we rely on Quadro P2000 video cards for our video workstations. Our video workstations are used video surveillance software. The software has been specifically written to use Nvidia for H.264 decoding. When the card hits 85% video engine load (name in GPUz) it will spread some of the workload to intel quick sync on the cpu. If quick sync hits 85% then it will move the workload directly to the CPU. The P2000 hits a good price point and it is easy to install more then one when it is needed. Is there a newer card out there at this price point that can do a handle more H.264 streams? If the card has a video engine load of 85% the GPU is at about 5-10% and is not used to decode the video.
Well you can benefit from the newer RTX cards based on Turing architecture and at this price point you can find GeForce RTX 2060 SUPER, but keep in mind that it is a gaming card and not a quadro.
Thank you for the feedback, it does not have to be a quadro card it just has to be Nvidia. The software only uses the part of the card that decodes H.264. When viewing Tech Power Up GPUz and I max out the card the only thing that registers with a load is the Video Engine Load. If the video engine load is at 85% the GPU only runs at about 10% utilization. The only thing I am looking for a card that can decode more H.264 streams than the Quadro P2000 at the same price point.
You can also use the more cheaper card like 1660ti orn1660 super which also has same nvenc chip as of RTX 2070. (Nvenc used for encoding)
hi, tried to connect you on facebook, but unable to do so.
can you share your fb profile to connect.
thanks
Tushar
The facebook url id is verma.akshat
Thanks Akshat ji
Well , I am an electronics engineer and understands the technology of read properly , currently I am trying to learn how the pascal architecture looks like and how does it work and how does Turing differs from pascal
It would be a great help is I can go through some detailed blog on this
Thanks
Tushar
Hello Tushar,
You can get into more details about the Pascal and Turing GPU architecture by going through the below mentioned whitepapers:
http://www2.maths.ox.ac.uk/~gilesm/cuda/lecs/Pascal_and_CUDA_8.0.pdf
https://images.nvidia.com/content/pdf/tesla/whitepaper/pascal-architecture-whitepaper.pdf
https://www.nvidia.com/content/dam/en-zz/Solutions/design-visualization/technologies/turing-architecture/NVIDIA-Turing-Architecture-Whitepaper.pdf
1> can u tell me the differance between of notebook card or desktop card ?
2> one more thing geforce 350 vs gtx 1050ti or 1650 which one is better?
3> geforce 350 , GTX1050ti ko beat kr skta hai kya?
please reply sir
thanks sir in advance…
In simpler terms, a laptop or notebook graphics card is the smaller version of desktop graphics card. It has lower TDP, lower clock speeds (most of the time) and almost no overclocking capability. A desktop graphics card performs better than its laptop version. GTX 1650 is the best of the lot and GTX 1050 Ti is better than GeForce MX350.
Hello. Sorry for question out of subject but as mechanical engineering student which one do you recommend? RTX 2060 or Quadro T1000 or any other laptop graphics card in this price range.
I would say RTX 2060 should be enough.
Hey
I am an architecture student ,
For an architecture student which of these would you recommend
Turing workstation graphic cards or gaming graphic cards ?
RTX 5000 , 6000, 8000 ( or ) RTX2080 , 2070
Do you mean between Quadro and GeForce RTX?
Yes
Quadro RTX ones will be better and stable but will cost more. If you have budget constraints then GeForce RTX will be fine too with Nvidia Studio Drivers.
Very well written and explained bhai. It helped me a lot to understand the first details of different types of GPU specifications. As a PhD scholar, I was really looking forward to understand what role does the better architectures of GPUs play in deep learning. Thanx for the information.
Thanks for the appreciation.